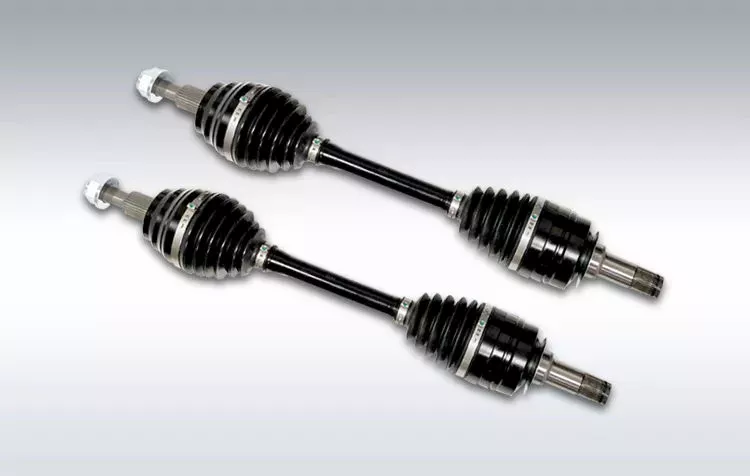
Product Description
Company Profile
HangZhou Xihu (West Lake) Dis. East Port Gear Manufacturing factory is located in Zhoujia Industrial Zone, CHINAMFG Town, HangZhou, 3km away from Xihu (West Lake) Dis.qian Lake. It focuses on precision gear research, development, production and sales. The factory has obtained ISO9001: 2015 certificate, IATF16949:2016. The main export markets were North America, South America and Europe. Products can be customized and mainly includes: New Energy Motor Shaft, Oil Pump Gear, Agricultural Machinery Gear, Transmission Gear, Electric Vehicle gear, etc. We are sincerely willing to cooperate with enterprises from all over the world.
Equipment And Main Products
Certifications
FAQ
Q1:How is the quality of your product?
A:Our product has reliable quality, high wear life
Q2:Customization process/work flow?
Advisory – Material selection – 2D/3D Drawing – Quotation – Payment – Production – Quality Control – Package – Delivery
Q3: What is your terms of packing?
A:Generally, we pack our goods in wooden cases, If you have special request about packing, pls negotiate with us in advance, we can pack the goods as your request.
Q4:Price?
A:We will offer competitive price after receiving your drawing
Q5:What is your terms of payment?
A:30% T/T advanced, 70% T/T before shipping
Q6:What is your terms of delivery?
A: FOB
Q7:What drawing software does your company use?
A:CAXA
Q8:Do you test all your goods before delivery?
A: Yes, we have 100% test before delivery
Q9:How about your delivery time?
A:Product can often be delivered within 40-90 days
Q10:Sample?
A:We offer paid sample.If you have sample requirements, please feel free to contact us at any time
Q11:What logistics packaging does your company use?
A:Express for urgent orders. UPS, FedEx, DHL, TNT, EMS.
Q12:Application range?
A:Automotive, medical, automation, agricultural, marine, etc.
Q13: How do you make our business long-term and good relationship?
A:1. We keep good quality and competitive price to ensure our customers benefit ;
2. We respect every customer as our friend and we sincerely do business and make friends with them,
no matter where they come from.
Parameter specifications
| Certification | Shipment | Quality | material | Company System Certification |
| IATF16949 | in time | high | steel | ISO9001 |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample customized version
|
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

How do PTO drivelines ensure efficient power transfer while maintaining operator safety?
PTO (Power Take-Off) drivelines are designed to ensure efficient power transfer while prioritizing operator safety. These drivelines incorporate various features and mechanisms to achieve both objectives. Let’s delve into the details:
1. Safety Shields and Guards:
PTO drivelines often include safety shields or guards to enclose the rotating components, such as the driveline shaft and universal joints. These shields are typically made of durable materials and are designed to prevent accidental contact with the moving parts, reducing the risk of entanglement or injury. Safety shields and guards serve as a physical barrier between the driveline and operators, ensuring operator safety while allowing power transfer to occur efficiently.
2. Shear Pins or Bolts:
Shear pins or bolts are commonly used in PTO drivelines to provide a safety measure against excessive loads or sudden obstructions. These pins or bolts are designed to break or shear off when the torque exceeds a certain threshold, disconnecting the driveline and preventing damage to the driveline components. By sacrificing themselves under high load conditions, shear pins or bolts protect the driveline from potential damage, ensuring operator safety and minimizing the need for costly repairs.
3. Slip Clutches:
Slip clutches are another safety feature incorporated into PTO drivelines. These clutches allow for a controlled slipping action when the torque exceeds a predetermined limit. The slipping action protects the driveline and driven equipment from sudden shock loads or excessive torque, preventing damage to the driveline components and reducing the risk of operator injury. Slip clutches provide a safety margin and help maintain efficient power transfer by momentarily disengaging the driveline until the excessive torque diminishes.
4. Overload Protection Devices:
Some PTO drivelines are equipped with overload protection devices, such as torque limiters or electronic control systems. These devices monitor the torque levels in the driveline and automatically disengage or limit power transmission when the torque exceeds a safe threshold. By preventing the driveline from operating under extreme loads, overload protection devices safeguard the driveline components and maintain operator safety. These devices can be reset or adjusted once the excessive load is removed, allowing power transfer to resume.
5. Constant Velocity (CV) Joints:
PTO drivelines that utilize constant velocity (CV) joints offer several safety benefits. CV joints maintain a constant angular velocity, regardless of the operating angle of the driveline, reducing vibration and power loss. By providing smooth power transmission, CV joints minimize the risk of sudden jolts or jerks that could endanger operators or compromise the stability of the driven equipment. The consistent power transfer facilitated by CV joints enhances both operator safety and the overall efficiency of the driveline.
6. Operator Training and Safety Practices:
While not directly built into the driveline itself, operator training and safety practices play a crucial role in ensuring safe and efficient PTO driveline operation. It is essential for operators to receive comprehensive training on the proper use, maintenance, and safety protocols associated with PTO drivelines. This training should include guidelines for safe engagement and disengagement of the driveline, understanding the importance of safety shields and guards, and recognizing potential hazards and risks during operation. By following recommended safety practices, operators can minimize the likelihood of accidents or injuries and maintain efficient power transfer.
By combining these features and promoting proper operator training, PTO drivelines achieve a balance between efficient power transfer and operator safety. The incorporation of safety shields, shear pins or bolts, slip clutches, overload protection devices, and CV joints helps prevent accidents, protect driveline components, and ensure the well-being of operators. It is crucial to adhere to manufacturer guidelines and industry safety standards to maximize the effectiveness of these safety measures and maintain a safe working environment.

Can you provide examples of machinery that utilize PTO drivelines for power transmission?
PTO (Power Take-Off) drivelines are widely used in various agricultural and industrial applications to transmit power from a power source, such as a tractor or engine, to driven machinery. Here are several examples of machinery that commonly utilize PTO drivelines for power transmission:
1. Agricultural Equipment:
– Tractor Implements: Numerous agricultural implements rely on PTO drivelines to receive power for their operation. Examples include rotary cutters, flail mowers, disc harrows, tillers, seeders, fertilizer spreaders, sprayers, hay balers, hay rakes, and hay tedders. These implements connect to the PTO shaft of a tractor, harnessing its power to perform tasks such as cutting, tilling, sowing, fertilizing, spraying, baling, and raking.
– Harvesting Equipment: Machinery used in harvesting, such as combines, forage harvesters, and grain augers, often utilize PTO drivelines to power their cutting and conveying mechanisms. The PTO driveline powers components like the cutter heads, threshing systems, and grain handling equipment, allowing for efficient harvesting and processing of crops.
– Forage and Silage Equipment: Equipment used for forage and silage production, including forage choppers, silage blowers, and silage wagons, commonly incorporate PTO drivelines. The driveline provides power for cutting and chopping forage crops and conveying them into storage or transport units.
– Irrigation Systems: PTO-driven irrigation systems, such as irrigation pumps and sprinkler systems, utilize PTO drivelines to power the pumps and drive the water distribution mechanisms. The PTO driveline allows for efficient water supply and irrigation in agricultural fields.
2. Construction and Earthmoving Equipment:
– Earth Augers: Earth augers used in construction and landscaping applications often rely on PTO drivelines for power transmission. PTO-driven augers are used for digging holes and installing posts, fences, and foundations.
– Post Hole Diggers: Post hole diggers, commonly used in fencing and construction projects, utilize PTO drivelines for power transmission. The driveline powers the digging mechanism, allowing for efficient digging of holes for post installation.
3. Industrial Equipment:
– Wood Chippers: Wood chippers used in the forestry and landscaping industries often incorporate PTO drivelines for power transmission. The PTO driveline powers the cutting and chipping mechanisms, enabling efficient processing of branches, logs, and other woody materials.
– Generators: PTO-driven generators are commonly used as backup power sources or in remote locations where electrical power is not readily available. The PTO driveline powers the generator, converting mechanical power into electrical power.
– Stationary Pumps: PTO drivelines are utilized in stationary pumps, such as water pumps, slurry pumps, and trash pumps. The PTO driveline drives the pump, allowing for the efficient transfer or movement of liquids or slurry.
– Industrial Mixers: PTO-driven mixers are used in various industries, including agriculture, food processing, and construction. The PTO driveline powers the mixing mechanism, facilitating the blending or agitation of materials.
– Hay Grinders: Hay grinders or tub grinders used in the agricultural and livestock industries often incorporate PTO drivelines for power transmission. The driveline powers the grinding mechanism, allowing for the processing of hay, straw, and other forage materials.
4. Specialty Equipment:
– Ice Resurfacers: Ice resurfacing machines, commonly used in ice rinks and winter sports facilities, often utilize PTO drivelines for power transmission. The driveline powers the ice resurfacing mechanism, ensuring a smooth and level ice surface.
– Snowblowers: Snowblowers or snow throwers used in snow removal operations can be equipped with PTO drivelines to power their cutting and throwing mechanisms. The PTO driveline enables efficient snow clearing by propelling and discharging snow.
– Street Sweepers: PTO-driven street sweepers are used for cleaning streets, parking lots, and other paved surfaces. The PTO driveline powers the sweeping brushes and collection system, facilitating effective debris removal.
These examples demonstrate the wide range of machinery that utilize PTO drivelines for power transmission in various industries. PTO drivelines provide a versatile and efficient means of transferring power, allowing for the operation of diverse equipment with a common power source.

Can you explain the types of PTO drivelines available and their specific applications?
PTO (Power Take-Off) drivelines come in various types and configurations, each designed to suit specific applications and equipment requirements. The choice of PTO driveline depends on factors such as power transmission needs, rotational speed, torque requirements, and the type of machinery being used. Let’s explore some of the commonly used types of PTO drivelines and their specific applications:
1. Non-Constant Velocity (Non-CV) PTO Driveline:
– Applications: Non-CV PTO drivelines are typically used for applications where the driven equipment operates at a constant speed and does not require smooth, continuous power transmission. They are commonly employed in tasks such as powering stationary equipment, grain augers, water pumps, and generators.
2. Constant Velocity (CV) PTO Driveline:
– Applications: CV PTO drivelines are designed for applications that require smooth and continuous power transmission, especially in situations where the driven equipment operates at varying angles or speeds. They are commonly used in tasks such as operating mowers, balers, combines, forage harvesters, and other equipment that involve rotational movement at different angles and speeds.
3. Shear Bolt PTO Driveline:
– Applications: Shear bolt PTO drivelines are primarily used to protect the driveline and driven equipment from excessive shock loads or sudden obstructions. They are commonly employed in tasks such as rotary cutters, flail mowers, and other implements that may encounter obstacles or tough vegetation. The shear bolts in the driveline are designed to break and disconnect the power transmission in case of excessive load, preventing damage to the driveline or equipment.
4. Slip Clutch PTO Driveline:
– Applications: Slip clutch PTO drivelines offer a means of protecting the driveline and driven equipment from excessive torque or sudden shock loads. They are commonly used in tasks such as rotary tillers, post hole diggers, and other implements where the equipment may encounter resistance or encounter obstacles. The slip clutch mechanism allows the driveline to slip or disengage momentarily when the torque exceeds a certain threshold, protecting against damage and allowing the equipment to continue operating once the resistance is removed.
5. Hydraulic PTO Driveline:
– Applications: Hydraulic PTO drivelines utilize hydraulic power instead of mechanical power transmission. They are commonly used in applications such as operating hydraulic pumps, winches, and other hydraulic-driven equipment. Hydraulic PTO drivelines are often found in industrial machinery, construction equipment, and vehicles where hydraulic power is readily available.
6. Front PTO Driveline:
– Applications: Front PTO drivelines are specifically designed for machinery with front-mounted implements or attachments. They are commonly used in tasks such as operating front-mounted mowers, snow blowers, or hydraulic front loaders. Front PTO drivelines enable power transmission to the front of the vehicle or equipment, allowing for efficient operation of front-mounted implements.
These are just some of the commonly used types of PTO drivelines and their specific applications. It’s important to note that the specific type of PTO driveline used may vary depending on the manufacturer, equipment design, and industry requirements. When selecting a PTO driveline, it’s crucial to consider the specific needs of the equipment and the intended application to ensure optimal performance, efficiency, and reliability.


editor by CX 2024-05-14
China Standard Drive Gear Pto and Transmission Shaft Factory Steel Precision Agricultural Machinery Use Power Transmission Shaft Transmission Shaft 118 PTO Driveline
Product Description
Parameter specifications
| Certification | Shipment | Quality | material | Company System Certification |
| IATF16949 | in time | high | steel | ISO9001 |
Company Profile
HangZhou Xihu (West Lake) Dis. East Port Gear Manufacturing factory is located in Zhoujia Industrial Zone, CHINAMFG Town, HangZhou, 3km away from Xihu (West Lake) Dis.qian Lake. It focuses on precision gear research, development, production and sales. The factory has obtained ISO9001: 2015 certificate, IATF16949:2016. The main export markets were North America, South America and Europe. Products can be customized and mainly includes: New Energy Motor Shaft, Oil Pump Gear, Agricultural Machinery Gear, Transmission Gear, Electric Vehicle gear, etc. We are sincerely willing to cooperate with enterprises from all over the world.
Equipment And Main Products
Certifications
FAQ
Q1:How is the quality of your product?
A:Our product has reliable quality, high wear life
Q2:Customization process/work flow?
Advisory – Material selection – 2D/3D Drawing – Quotation – Payment – Production – Quality Control – Package – Delivery
Q3: What is your terms of packing?
A:Generally, we pack our goods in wooden cases, If you have special request about packing, pls negotiate with us in advance, we can pack the goods as your request.
Q4:Price?
A:We will offer competitive price after receiving your drawing
Q5:What is your terms of payment?
A:30% T/T advanced, 70% T/T before shipping
Q6:What is your terms of delivery?
A: FOB
Q7:What drawing software does your company use?
A:CAXA
Q8:Do you test all your goods before delivery?
A: Yes, we have 100% test before delivery
Q9:How about your delivery time?
A:Product can often be delivered within 40-90 days
Q10:Sample?
A:We offer paid sample.If you have sample requirements, please feel free to contact us at any time
Q11:What logistics packaging does your company use?
A:Express for urgent orders. UPS, FedEx, DHL, TNT, EMS.
Q12:Application range?
A:Automotive, medical, automation, agricultural, marine, etc.
Q13: How do you make our business long-term and good relationship?
A:1. We keep good quality and competitive price to ensure our customers benefit ;
2. We respect every customer as our friend and we sincerely do business and make friends with them,
no matter where they come from.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Alloy Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample customized version
|
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

How do manufacturers ensure the compatibility of PTO drivelines with diverse equipment?
Manufacturers employ various methods and considerations to ensure the compatibility of PTO (Power Take-Off) drivelines with diverse equipment. Here are the key factors they take into account:
1. Standardization:
– PTO drivelines are built according to standardized specifications and dimensions. Manufacturers adhere to industry standards and guidelines, such as those set by organizations like the American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers (ASABE) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). These standards define key parameters like shaft dimensions, connection types, torque ratings, and safety requirements. By following these standards, manufacturers ensure that their PTO drivelines can be easily interchanged and connected with diverse equipment that adheres to the same standards.
2. Compatibility Testing:
– Manufacturers conduct extensive compatibility testing to verify the performance and suitability of their PTO drivelines with different types of equipment. This testing involves connecting the drivelines to various implements, machines, and power sources to assess factors like power transfer efficiency, alignment, torque handling, and safety. Compatibility testing helps identify any issues or limitations that may arise when connecting the drivelines to different equipment. Manufacturers can then make necessary adjustments or recommendations to ensure optimal compatibility.
3. Application-Specific Design:
– Manufacturers often design PTO drivelines with specific applications in mind. They consider the requirements and operating conditions of various equipment categories, such as agricultural machinery, construction equipment, or industrial machinery. Manufacturers may offer different models or configurations of PTO drivelines tailored to these specific applications. For example, agricultural PTO drivelines may have features like enhanced dust resistance, rugged construction, and additional safety measures, while industrial PTO drivelines may prioritize high torque capacity and durability for heavy-duty applications. By designing drivelines with application-specific considerations, manufacturers ensure that their products meet the unique demands of diverse equipment types.
4. Consultation and Collaboration:
– Manufacturers maintain close relationships and collaborations with equipment manufacturers and suppliers. This collaboration allows them to exchange information about equipment requirements and driveline specifications. By understanding the specific needs of different equipment, manufacturers can develop PTO drivelines that align with those requirements. They may also provide technical support and guidance to equipment manufacturers regarding the selection and integration of PTO drivelines into their products. This consultation and collaboration foster compatibility and ensure that the drivelines are suitable for the intended equipment.
5. Documentation and Guidelines:
– Manufacturers provide detailed documentation, user manuals, and guidelines that outline the compatibility aspects of their PTO drivelines. These resources specify the recommended equipment types, connection methods, torque limits, and other important considerations for proper integration. Operators and equipment manufacturers can refer to these documents to ensure the compatibility of the PTO drivelines with diverse equipment. Manufacturers may also offer technical support or customer service channels to address any compatibility-related questions or concerns.
6. Ongoing Research and Development:
– Manufacturers continuously invest in research and development to improve the compatibility of their PTO drivelines with evolving equipment technologies. They stay updated with industry trends, technological advancements, and changing equipment requirements. This allows them to adapt and innovate their driveline designs, materials, and manufacturing processes to ensure ongoing compatibility with new and emerging equipment types and applications.
In summary, manufacturers ensure the compatibility of PTO drivelines with diverse equipment through standardization, compatibility testing, application-specific design, consultation and collaboration with equipment manufacturers, documentation and guidelines, and ongoing research and development. These efforts enable manufacturers to provide drivelines that effectively and safely interface with a wide range of equipment, promoting seamless integration and reliable power transfer.

Are there any limitations or challenges associated with using PTO driveline systems?
While PTO (Power Take-Off) driveline systems offer numerous benefits, there are also certain limitations and challenges associated with their use. Here are some of the key considerations:
1. Safety Risks:
– PTO driveline systems can pose safety risks if not handled properly. The rotating components of the driveline, such as the shafts, yokes, and universal joints, can cause serious injuries if operators come into contact with them while in motion. It is crucial to follow proper safety procedures, including the use of shields, guards, and safety devices, to prevent accidents. Adequate training and awareness about the potential hazards associated with PTO driveline systems are essential.
2. Maintenance and Lubrication:
– PTO driveline systems require regular maintenance and lubrication to ensure optimal performance and longevity. The universal joints, splines, and other moving parts need to be inspected, cleaned, and properly lubricated according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Neglecting maintenance can lead to premature wear, increased friction, and potential failures, compromising the driveline’s efficiency and reliability.
3. Alignment and Misalignment:
– Proper alignment between the power source and the driven equipment is crucial for efficient power transfer in PTO driveline systems. Misalignment can result in increased vibration, excessive wear, and reduced power transmission efficiency. Achieving and maintaining proper alignment can be challenging, especially when connecting the driveline to equipment with varying mounting heights, angles, or misaligned driveline components. Operators need to carefully align the driveline to minimize stress and ensure smooth operation.
4. Length and Compatibility:
– PTO driveline systems need to be appropriately sized and compatible with the specific equipment and applications they are intended for. Variations in length, connection types, and torque requirements among different equipment can pose challenges in selecting the right driveline. Ensuring proper compatibility and fit between the driveline and the equipment is crucial for optimal power transmission and safety. Customization or adaptation may be necessary in certain cases, which could add complexity and cost.
5. Torque Overload and Protection:
– PTO driveline systems are susceptible to torque overload, especially when the driven equipment encounters sudden resistance or obstructions. Excessive torque can lead to driveline component failures, such as universal joint breakage or shear pin failure, potentially causing damage to the driveline or other connected components. Proper protection mechanisms, such as shear pins, slip clutches, or overload clutches, should be employed to prevent damage and ensure operator safety.
6. Noise and Vibration:
– PTO driveline systems can generate significant noise and vibration during operation. The rotating components, imbalances, misalignments, or worn-out components can contribute to increased noise levels and vibration. Excessive noise and vibration not only affect operator comfort but can also lead to component fatigue and premature wear. Employing appropriate vibration dampening techniques, balancing the driveline components, and using vibration-absorbing materials can help mitigate these issues.
7. Environmental Factors:
– PTO driveline systems may be exposed to various environmental factors, such as dust, debris, moisture, and temperature extremes. These factors can impact the driveline’s performance and longevity. Dust and debris can accumulate in the driveline components, leading to increased friction and wear. Moisture and corrosive environments can cause rust and degradation of driveline parts. Extreme temperatures can affect the lubrication properties and material integrity. Regular inspection, cleaning, and appropriate protection measures are essential to mitigate the impact of environmental factors.
In summary, while PTO driveline systems offer significant advantages, there are limitations and challenges that need to be addressed for safe and efficient operation. These include safety risks, maintenance requirements, alignment considerations, compatibility issues, torque overload protection, noise and vibration management, and the impact of environmental factors. By understanding and addressing these challenges, operators can ensure the proper functioning and longevity of PTO driveline systems.

What are the key components of a PTO driveline system and how do they work together?
A PTO (Power Take-Off) driveline system consists of several key components that work together to facilitate power transmission from a power source to driven equipment. Each component plays a specific role in ensuring the efficient and reliable transfer of rotational power. Let’s explore the key components of a PTO driveline system and how they work together:
1. Power Source:
The power source in a PTO driveline system is typically an engine or motor, such as the one found in a tractor or industrial machine. The power source generates rotational power, which serves as the energy source for the entire system. The power generated by the engine is harnessed and transferred to the PTO driveline for further transmission.
2. PTO Shaft:
The PTO shaft is a rotating shaft that extends from the power source to the driven equipment. It is the primary component responsible for transmitting power from the power source to the implement. The PTO shaft is connected to the power source at one end, typically through a PTO coupling, and to the driven equipment at the other end. As the power source rotates, the rotational motion is transferred along the PTO shaft to drive the implement.
3. PTO Clutch:
The PTO clutch is a mechanism that allows the operator to engage or disengage the power transfer between the power source and the driven equipment. It is usually controlled by a lever or switch within easy reach of the operator. When the PTO clutch is engaged, the power from the power source is transmitted through the PTO shaft to the implement. Conversely, disengaging the PTO clutch interrupts the power transfer, ensuring that power is only transmitted when needed. The PTO clutch provides control and safety during operation, allowing the operator to start or stop power transmission as required.
4. PTO Gearbox:
Some machinery may incorporate a PTO gearbox between the power source and the PTO shaft. The PTO gearbox is responsible for adjusting the rotational speed and torque of the power transfer. It contains a set of gears that can be switched or adjusted to modify the speed and torque output of the PTO shaft. By changing the gear ratios, the PTO gearbox allows operators to adapt the power transmission to suit different implements or tasks. This enables the use of implements that require varying rotational speeds or different levels of torque, enhancing the versatility of the PTO driveline system.
5. PTO Driven Equipment:
The driven equipment refers to the implements or machinery that receive power from the PTO driveline system. This can include a wide range of equipment, such as mowers, balers, sprayers, augers, pumps, or generators. The PTO driveline system transfers rotational power from the power source through the PTO shaft to the driven equipment, enabling them to perform their specific functions. The driven equipment may have input shafts or connections designed to receive the PTO shaft and convert the rotational power into the desired output, such as cutting, baling, spraying, or generating electricity.
These key components of a PTO driveline system work together in a coordinated manner to achieve effective power transmission. The power generated by the engine is transferred through the PTO clutch to the PTO shaft. If a PTO gearbox is present, it can adjust the speed and torque of the power before it reaches the driven equipment. The PTO shaft then transmits the rotational power to the driven equipment, allowing them to perform their intended functions. The operator has control over the power transmission process through the PTO clutch, enabling them to start or stop the power transfer as needed.
Overall, the key components of a PTO driveline system collaborate to provide a reliable and efficient means of power transmission from the power source to the driven equipment. This facilitates a wide range of agricultural and industrial applications, enhancing the functionality, versatility, and productivity of machinery in these sectors.


editor by CX 2024-05-03
China Best Sales Customized High Precision Spare Parts Auto/Truck/Drive/Gear/Spline/Propeller/Half/Sleeve/Machinery/Sliding/Transmission Axle Shaft 42CrMo 20crmoti Drive Line
Product Description
Customized High Precision Spare Parts Auto/Truck/Drive/Gear/Spline/Propeller/Half/Sleeve/Machinery/Sliding/Transmission Axle Shaft 42CrMo 20CrMoTi
(1) Accessory products of the truck, the product quality is stable and reliable.
(2) Forged with 42CrMo material and heat treated and tempered for 32 degrees, so that the half shaft has stronger toughness and is not easy to break and bend.
(3) Processed in the machining center, ensure that the products have rigorous dimensional coordinates to ensure 100% qualified rate of products.
(4) Products are inspected 1 by 1 and delivered out of the warehouse, with unified laser identification to ensure product traceability.
(5) Various sizes of axle shafts can be customized to meet customer needs.
(6) The unified brand carton, inner bag and integral foam packaging, which is strong and beautiful.
Factory Show
More Products
| Truck Model | Sinotruk, Shacman, CZPT Auman, CZPT Xihu (West Lake) Dis., Xihu (West Lake) Dis.feng, Xihu (West Lake) Dis.feng Liuqi Balong, North BENZ( BEIBEN), C&C, JAC, etc. | |
| Product catalogue | Axle | Wheel Assembly |
| Differential Assembly | ||
| Main Reducer Assembly | ||
| Inner Ring Gear& Bracket | ||
| Basin Angle Gear/ Bevel Gear | ||
| Axle Shaft/ Half Shaft & Through Shaft | ||
| Axle Housing& Axle Assembly | ||
| Steering knuckle & Front Axle | ||
| Gear | ||
| Brake Drum& Wheel Hub | ||
| Flange | ||
| Bearing | ||
| Main Reducer Housing | ||
| Oil Seal Seat | ||
| Nut& Shim Series | ||
| Brake Backing Plate | ||
| Chassis Support Products | Leaf Spring Bracket | |
| Drop Arm Series | ||
| Bracket Series | ||
| Leaf Spring Shackle Series | ||
| Balanced Suspension Series | Balance Shaft Assembly | |
| Balance Shaft Housing | ||
| Axle Spring Seat | ||
| Thrust Rod | ||
| Balance Shaft Parts | ||
| Shock Absorber Series | Shock Absorber | |
| Shock Absorbing Airbag | ||
| Steering System | Power Steering Pump | |
| Power Steering Gear | ||
| Rubber Products | Oil Seal | |
| Rubber Support | ||
| Thrust Rod Rubber Core | ||
| Truck Belt | ||
| Engine support | ||
| Other | ||
| Clutch Series | Clutch Pressure Plate | |
| Clutch Disc | ||
| Flywheel Assembly | ||
| Flywheel Ring Gear | ||
| Adjusting Arm Series | ||
Function
Heavy trucks usually have double rear axles. If they are driven separately, they need to use 2 transmission shafts or add a transfer case at the output of the gearbox, which is heavy and cumbersome. Now a through shaft is designed in the middle axle to solve this problem. Only 1 transmission shaft is needed to drive 2 rear axles at the same time.
Packaging & Shipping
Exhibition
FAQ
Q1. Are you a factory or trading company?
We are a factory integrating research, development, production and sales.
Q2. What are the advantages of your products?
We support product customization to meet customer needs for special products. We can strictly control the products from raw materials to production, processing, product quality inspection, delivery, packaging, etc., and provide customers with high-end products and the most advantageous prices.
Q3. How about products price?
We are a factory, all products are direct sale at factory price. For the same price, we will provide the best quality; for the same quality, we have the most advantageous price.
Q4. What is your terms of packing?
We have branded packaging and neutral packaging, and we can also do what you want with authorization. This is flexible.
Q5. How to guarantee your after-sales service?
Strict inspection during production, Strictly check the products before shipment to ensure our packaging in good condition. Track and receive feedback from customer regularly. Our products warranty is 365 days.
Each product provides quality assurance service. If there is a problem with the product within the warranty period, the customer can negotiate with us in detail about the related claims, and we will do our best to satisfy the customer.
Certifications
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | 45#Steel, 42CrMo, 20crmoti |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | High Precision |
| Samples: |
US$ 29/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
| Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|
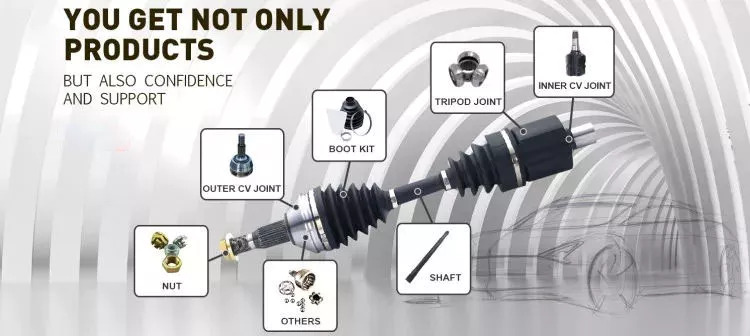
What factors should be considered when designing an efficient driveline system?
Designing an efficient driveline system involves considering various factors that contribute to performance, reliability, and overall system efficiency. Here are the key factors that should be considered when designing an efficient driveline system:
1. Power Requirements:
The power requirements of the vehicle play a crucial role in designing an efficient driveline system. It is essential to determine the maximum power output of the engine and ensure that the driveline components can handle and transfer that power efficiently. Optimizing the driveline for the specific power requirements helps minimize energy losses and maximize overall efficiency.
2. Weight and Packaging:
The weight and packaging of the driveline components have a significant impact on system efficiency. Lightweight materials and compact design help reduce the overall weight of the driveline, which can improve fuel efficiency and vehicle performance. Additionally, efficient packaging ensures that driveline components are properly integrated, minimizing energy losses and maximizing available space within the vehicle.
3. Friction and Mechanical Losses:
Minimizing friction and mechanical losses within the driveline system is crucial for achieving high efficiency. Frictional losses occur at various points, such as bearings, gears, and joints. Selecting low-friction materials, optimizing lubrication systems, and implementing efficient bearing designs can help reduce these losses. Additionally, employing advanced gear designs, such as helical or hypoid gears, can improve gear mesh efficiency and reduce power losses.
4. Gear Ratios and Transmission Efficiency:
The selection of appropriate gear ratios and optimizing transmission efficiency greatly impacts driveline efficiency. Gear ratios should be chosen to match the vehicle’s power requirements, driving conditions, and desired performance characteristics. In addition, improving the efficiency of the transmission, such as reducing gear mesh losses and enhancing hydraulic or electronic control systems, can contribute to overall driveline efficiency.
5. Aerodynamic Considerations:
Aerodynamics play a significant role in a vehicle’s overall efficiency, including the driveline system. Reducing aerodynamic drag through streamlined vehicle design, efficient cooling systems, and appropriate underbody airflow management can enhance driveline efficiency by reducing the power required to overcome air resistance.
6. System Integration and Control:
Efficient driveline design involves seamless integration and control of various components. Employing advanced control systems, such as electronic control units (ECUs), can optimize driveline operation by adjusting power distribution, managing gear shifts, and optimizing torque delivery based on real-time driving conditions. Effective system integration ensures smooth communication and coordination between driveline components, improving overall efficiency.
7. Environmental Considerations:
Environmental factors should also be taken into account when designing an efficient driveline system. Considerations such as emissions regulations, sustainability goals, and the use of alternative power sources (e.g., hybrid or electric drivetrains) can influence driveline design decisions. Incorporating technologies like regenerative braking or start-stop systems can further enhance efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
8. Reliability and Durability:
Designing an efficient driveline system involves ensuring long-term reliability and durability. Selecting high-quality materials, performing thorough testing and validation, and considering factors such as thermal management and component durability help ensure that the driveline system operates efficiently over its lifespan.
By considering these factors during the design process, engineers can develop driveline systems that are optimized for efficiency, performance, and reliability, resulting in improved fuel economy, reduced emissions, and enhanced overall vehicle efficiency.

Are there any limitations or disadvantages associated with driveline systems?
While driveline systems offer numerous advantages in terms of power transmission and vehicle performance, there are also some limitations and disadvantages associated with their use. It’s important to consider these factors when designing, operating, and maintaining driveline systems. Let’s explore some of the limitations and disadvantages:
1. Complex Design and Integration:
Driveline systems can be complex in design, especially in modern vehicles with advanced technologies. They often consist of multiple components, such as transmissions, differentials, transfer cases, and drive shafts, which need to be properly integrated and synchronized. The complexity of the driveline system can increase manufacturing and assembly challenges, as well as the potential for compatibility issues or failures if not designed and integrated correctly.
2. Energy Losses:
Driveline systems can experience energy losses during power transmission. These losses occur due to factors such as friction, heat generation, mechanical inefficiencies, and fluid drag in components like gearboxes, differentials, and torque converters. The energy losses can negatively impact overall efficiency and result in reduced fuel economy or power output, especially in systems with multiple driveline components.
3. Limited Service Life and Maintenance Requirements:
Driveline components, like any mechanical system, have a limited service life and require regular maintenance. Components such as clutches, bearings, gears, and drive shafts are subject to wear and tear, and may need to be replaced or repaired over time. Regular maintenance, including lubrication, adjustments, and inspections, is necessary to ensure optimal performance and prevent premature failures. Failure to perform proper maintenance can lead to driveline malfunctions, increased downtime, and costly repairs.
4. Weight and Space Constraints:
Driveline systems add weight and occupy space within a vehicle. The additional weight affects fuel efficiency and overall vehicle performance. Moreover, the space occupied by driveline components can limit design flexibility, particularly in compact or electric vehicles where space optimization is crucial. Manufacturers must strike a balance between driveline performance, vehicle weight, and available space to meet the requirements of each specific vehicle type.
5. Noise, Vibration, and Harshness (NVH):
Driveline systems can generate noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH) during operation. Factors such as gear meshing, unbalanced rotating components, or improper driveline alignment can contribute to unwanted vibrations or noise. NVH issues can affect driving comfort, passenger experience, and vehicle refinement. Manufacturers employ various techniques, including vibration dampening materials, isolators, and precision engineering, to minimize NVH levels, but achieving complete elimination can be challenging.
6. Limited Torque Handling Capability:
Driveline systems have limitations in terms of torque handling capability. Excessive torque beyond the rated capacity of driveline components can lead to failures, such as shearing of gears, clutch slippage, or drive shaft breakage. High-performance vehicles or heavy-duty applications may require specialized driveline components capable of handling higher torque loads, which can increase costs and complexity.
7. Traction Limitations:
Driveline systems, particularly in vehicles with two-wheel drive configurations, may experience traction limitations, especially in slippery or off-road conditions. Power is typically transmitted to only one or two wheels, which can result in reduced traction and potential wheel slippage. This limitation can be mitigated by utilizing technologies such as limited-slip differentials, electronic traction control, or implementing all-wheel drive systems.
While driveline systems provide crucial power transmission and vehicle control, they do have limitations and disadvantages that need to be considered. Manufacturers, designers, and operators should carefully assess these factors and implement appropriate design, maintenance, and operational practices to optimize driveline performance, reliability, and overall vehicle functionality.

Which industries and vehicles commonly use drivelines for power distribution?
Drivelines are widely used in various industries and vehicles for power distribution. They play a crucial role in transmitting power from the engine or power source to the driven components, enabling motion and torque transfer. Here’s a detailed explanation of the industries and vehicles that commonly utilize drivelines for power distribution:
1. Automotive Industry: The automotive industry extensively utilizes drivelines in passenger cars, commercial vehicles, and off-road vehicles. Drivelines are a fundamental component of vehicles, enabling power transmission from the engine to the wheels. They are found in a range of vehicle types, including sedans, SUVs, pickup trucks, vans, buses, and heavy-duty trucks. Drivelines in the automotive industry are designed to provide efficient power distribution, enhance vehicle performance, and ensure smooth acceleration and maneuverability.
2. Agricultural Industry: Drivelines are essential in the agricultural industry for various farming machinery and equipment. Tractors, combines, harvesters, and other agricultural machinery rely on drivelines to transfer power from the engine to the wheels or tracks. Drivelines in agricultural equipment often incorporate power take-off (PTO) units, allowing the connection of implements such as plows, seeders, and balers. These drivelines are designed to handle high torque loads, provide traction in challenging field conditions, and facilitate efficient farming operations.
3. Construction and Mining Industries: Drivelines are extensively used in construction and mining equipment, where they enable power distribution and mobility in heavy-duty machinery. Excavators, bulldozers, wheel loaders, dump trucks, and other construction and mining vehicles rely on drivelines to transfer power from the engine to the wheels or tracks. Drivelines in these industries are designed to withstand rigorous operating conditions, deliver high torque and traction, and provide the necessary power for excavation, hauling, and material handling tasks.
4. Industrial Equipment: Various industrial equipment and machinery utilize drivelines for power distribution. This includes material handling equipment such as forklifts and cranes, industrial trucks, conveyor systems, and industrial vehicles used in warehouses, factories, and distribution centers. Drivelines in industrial equipment are designed to provide efficient power transmission, precise control, and maneuverability in confined spaces, enabling smooth and reliable operation in industrial settings.
5. Off-Road and Recreational Vehicles: Drivelines are commonly employed in off-road and recreational vehicles, including all-terrain vehicles (ATVs), side-by-side vehicles (UTVs), dirt bikes, snowmobiles, and recreational boats. These vehicles require drivelines to transfer power from the engine to the wheels, tracks, or propellers, enabling off-road capability, traction, and water propulsion. Drivelines in off-road and recreational vehicles are designed for durability, performance, and enhanced control in challenging terrains and recreational environments.
6. Railway Industry: Drivelines are utilized in railway locomotives and trains for power distribution and propulsion. They are responsible for transmitting power from the locomotive’s engine to the wheels or driving systems, enabling the movement of trains on tracks. Drivelines in the railway industry are designed to handle high torque requirements, ensure efficient power transfer, and facilitate safe and reliable train operation.
7. Marine Industry: Drivelines are integral components in marine vessels, including boats, yachts, ships, and other watercraft. Marine drivelines are used for power transmission from the engine to the propellers or water jets, providing thrust and propulsion. They are designed to withstand the corrosive marine environment, handle high torque loads, and ensure efficient power transfer for marine propulsion.
These are some of the industries and vehicles that commonly rely on drivelines for power distribution. Drivelines are versatile components that enable efficient power transmission, mobility, and performance across a wide range of applications, contributing to the functionality and productivity of various industries and vehicles.


editor by CX 2024-04-25
China Hot selling Precision Transmission /Drive/Axle/Auto/Spline/Machinery Parts/ Rotor Gear Customized Machining Knurling Shaft Drive Line
Product Description
Precision Shaft by CNC Turning Machining
Our advantage:
*Specialization in CNC formulations of high precision and quality
*Independent quality control department
*Control plan and process flow sheet for each batch
*Quality control in all whole production
*Meeting demands even for very small quantities or single units
*Short delivery times
*Online orders and production progress monitoring
*Excellent price-quality ratio
*Absolute confidentiality
*Various materials (stainless steel, iron, brass, aluminum, titanium, special steels, industrial plastics)
*Manufacturing of complex components of 1 – 1000mm.
Production machine:
Inspection equipment :
Certificate:
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Material: | Carbon Steel |
|---|---|
| Load: | Drive Shaft |
| Stiffness & Flexibility: | Stiffness / Rigid Axle |
| Journal Diameter Dimensional Accuracy: | IT01-IT5 |
| Axis Shape: | Straight Shaft |
| Shaft Shape: | Real Axis |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|

How do manufacturers ensure the compatibility of driveline components with different vehicles?
Manufacturers employ various measures to ensure the compatibility of driveline components with different vehicles. These measures involve careful design, engineering, testing, and standardization processes to meet the specific requirements of each vehicle type. Let’s explore how manufacturers ensure compatibility:
1. Vehicle-Specific Design:
Manufacturers design driveline components with specific vehicle types in mind. Each vehicle type, such as passenger cars, trucks, SUVs, or commercial vehicles, has unique requirements in terms of power output, torque capacity, weight distribution, space constraints, and intended usage. Manufacturers consider these factors during the component design phase to ensure that the driveline components are optimized for compatibility with the intended vehicle type.
2. Engineering and Simulation:
Manufacturers employ advanced engineering techniques and simulation tools to evaluate the performance and compatibility of driveline components. They use computer-aided design (CAD) software and finite element analysis (FEA) simulations to model and analyze the behavior of the components under various operating conditions. This allows them to identify any potential compatibility issues, such as excessive stress, misalignment, or interference, and make necessary design adjustments before moving to the production stage.
3. Prototyping and Testing:
Manufacturers create prototypes of driveline components and subject them to rigorous testing to ensure compatibility. These tests include bench testing, dynamometer testing, and vehicle-level testing. By simulating real-world operating conditions, manufacturers can evaluate the performance, durability, and compatibility of the components. They assess factors such as power transmission efficiency, torque capacity, heat dissipation, noise and vibration levels, and overall drivability to ensure that the components meet the requirements and are compatible with the intended vehicle.
4. Standardization:
Manufacturers adhere to industry standards and specifications to ensure compatibility and interchangeability of driveline components. These standards cover various aspects such as dimensions, material properties, spline profiles, shaft diameters, and mounting interfaces. By following established standards, manufacturers can ensure that their driveline components can be seamlessly integrated into different vehicles from various manufacturers, promoting compatibility and ease of replacement or upgrade.
5. Collaborative Development:
Manufacturers often collaborate closely with vehicle manufacturers during the development process to ensure compatibility. This collaboration involves sharing specifications, design requirements, and performance targets. By working together, driveline manufacturers can align their component designs with the vehicle manufacturer’s specifications, ensuring that the driveline components fit within the vehicle’s space constraints, mating interfaces, and intended usage. This collaborative approach helps optimize compatibility and integration between the driveline components and the vehicle’s overall system.
6. Continuous Improvement:
Manufacturers continuously improve their driveline components based on feedback, field data, and advancements in technology. They gather information from vehicle manufacturers, end-users, and warranty claims to identify any compatibility issues or performance shortcomings. This feedback loop helps drive refinements and enhancements in the design, manufacturing processes, and material selection of the driveline components, ensuring better compatibility and performance in future iterations.
Overall, manufacturers employ a combination of vehicle-specific design, engineering and simulation, prototyping and testing, standardization, collaborative development, and continuous improvement to ensure the compatibility of driveline components with different vehicles. These efforts help optimize power transmission, reliability, and performance, while ensuring a seamless integration of the driveline components into the diverse range of vehicles present in the market.

How do drivelines enhance the performance of different types of vehicles?
Drivelines significantly contribute to enhancing the performance of different types of vehicles by optimizing power delivery, improving traction, and tailoring the driving characteristics to suit specific needs. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drivelines enhance performance in various vehicle types:
1. Passenger Cars:
In passenger cars, driveline configurations, such as front-wheel drive (FWD), rear-wheel drive (RWD), and all-wheel drive (AWD), play a crucial role in performance. Here’s how drivelines enhance performance in passenger cars:
- FWD: Front-wheel drive systems provide better traction and stability, particularly in adverse weather conditions. FWD drivelines distribute weight more evenly over the front wheels, resulting in improved grip during acceleration and cornering.
- RWD: Rear-wheel drive drivelines offer better weight distribution, allowing for improved handling and balanced performance. RWD vehicles typically exhibit better acceleration and a more engaging driving experience, especially in performance-oriented cars.
- AWD: All-wheel drive drivelines deliver power to all four wheels, improving traction and stability in various driving conditions. AWD systems enhance performance by maximizing grip and providing optimal power distribution between the front and rear wheels.
2. Sports Cars and Performance Vehicles:
Driveline systems in sports cars and performance vehicles are designed to enhance acceleration, handling, and overall driving dynamics. Key features include:
- Rear-Wheel Drive (RWD): RWD drivelines are often favored in sports cars for their ability to deliver power to the rear wheels, resulting in better weight transfer during acceleration and improved handling characteristics.
- Performance-oriented AWD: Some high-performance vehicles employ advanced AWD systems that can variably distribute torque between the front and rear wheels. These systems enhance traction, stability, and cornering capabilities, allowing for superior performance on both dry and slippery surfaces.
- Torque Vectoring: Certain driveline systems incorporate torque vectoring technology, which actively varies the torque distribution between wheels. This enables precise control during cornering, reducing understeer and enhancing agility and stability.
3. Off-Road Vehicles:
Drivelines in off-road vehicles are designed to provide exceptional traction, durability, and maneuverability in challenging terrains. Key features include:
- Four-Wheel Drive (4WD) and All-Wheel Drive (AWD): 4WD and AWD drivelines are commonly used in off-road vehicles to improve traction on uneven surfaces. These drivelines distribute power to all wheels, allowing for better grip and enhanced off-road capability.
- Differential Locks: Off-road drivelines often incorporate differential locks that can be engaged to lock the wheels on an axle together. This feature ensures that power is evenly distributed to all wheels, maximizing traction and overcoming challenging obstacles.
- High Ground Clearance: Drivelines in off-road vehicles are designed to accommodate higher ground clearance, allowing for improved approach, departure, and breakover angles. This design feature enhances the vehicle’s ability to navigate over rough terrain without damaging the driveline components.
4. Trucks and Commercial Vehicles:
Drivelines in trucks and commercial vehicles are engineered to provide high torque delivery, durability, and efficiency. Key features include:
- High Torque Handling: Drivelines in trucks and commercial vehicles are designed to handle high torque outputs from powerful engines, enabling efficient towing, hauling, and overall performance.
- Transmission Options: Drivelines in trucks often feature transmissions with multiple gear ratios, allowing drivers to select the appropriate gear for different load conditions. This enhances performance, fuel efficiency, and overall drivability.
- Efficient Power Transfer: Drivelines in commercial vehicles focus on maximizing power transfer efficiency, minimizing energy losses, and optimizing fuel economy. This is achieved through the use of efficient transmission designs, low-friction components, and advanced control systems.
5. Electric and Hybrid Vehicles:
Drivelines in electric and hybrid vehicles play a crucial role in delivering power from the electric motor(s) to the wheels. Key features include:
- Instant Torque: Electric drivelines offer instant torque delivery, providing quick acceleration andresponsive performance. This enhances the driving experience and allows for swift overtaking and merging.
- Regenerative Braking: Electric and hybrid drivelines can incorporate regenerative braking systems, which convert kinetic energy during braking into electrical energy. This improves overall efficiency and extends the vehicle’s range.
- Multi-Motor Systems: Some electric and hybrid drivelines utilize multiple motors to drive different axles or wheels independently. This enables advanced torque vectoring and enhances handling, stability, and traction control.
These are just a few examples of how drivelines enhance the performance of different types of vehicles. Driveline configurations, technologies, and engineering considerations are tailored to each vehicle type, optimizing power delivery, handling, traction, and other performance characteristics specific to their intended use and market segment.

What benefits do drivelines offer for different types of vehicles and equipment?
Drivelines offer several benefits for different types of vehicles and equipment across various industries. They play a critical role in power transmission, mobility, efficiency, and overall performance. Here’s a detailed explanation of the benefits drivelines offer for different types of vehicles and equipment:
1. Power Transmission: Drivelines are designed to efficiently transmit power from the engine or power source to the driven components, such as wheels, tracks, implements, or machinery. They ensure the smooth transfer of torque, allowing vehicles and equipment to generate the necessary power for propulsion, lifting, hauling, or other tasks. By effectively transmitting power, drivelines maximize the performance and productivity of vehicles and equipment.
2. Mobility and Maneuverability: Drivelines enable vehicles and equipment to achieve mobility and maneuverability across various terrains and working conditions. By transmitting power to the wheels or tracks, drivelines provide the necessary traction and control to overcome obstacles, navigate uneven surfaces, and operate in challenging environments. They contribute to the overall stability, handling, and agility of vehicles and equipment, allowing them to move efficiently and safely.
3. Versatility and Adaptability: Drivelines offer versatility and adaptability for different types of vehicles and equipment. They can be designed and configured to meet specific requirements, such as front-wheel drive, rear-wheel drive, four-wheel drive, or all-wheel drive systems. This flexibility allows vehicles and equipment to adapt to various operating conditions, including normal roads, off-road terrains, agricultural fields, construction sites, or industrial facilities. Drivelines also accommodate different power sources, such as internal combustion engines, electric motors, or hybrid systems, enhancing the adaptability of vehicles and equipment.
4. Efficiency and Fuel Economy: Drivelines contribute to efficiency and fuel economy in vehicles and equipment. They optimize power transmission by utilizing appropriate gear ratios, minimizing energy losses, and improving overall system efficiency. Drivelines with advanced technologies, such as continuously variable transmissions (CVTs) or automated manual transmissions (AMTs), can further enhance efficiency by continuously adjusting gear ratios based on load and speed conditions. Efficient driveline systems help reduce fuel consumption, lower emissions, and maximize the operational range of vehicles and equipment.
5. Load Carrying Capacity: Drivelines are designed to handle and transmit high torque and power, enabling vehicles and equipment to carry heavy loads. They incorporate robust components, such as heavy-duty axles, reinforced drive shafts, and durable differentials, to withstand the demands of load-bearing applications. Drivelines ensure the reliable transmission of power, allowing vehicles and equipment to transport materials, tow trailers, or carry payloads efficiently and safely.
6. Safety and Control: Drivelines contribute to safety and control in vehicles and equipment. They enable precise control over acceleration, deceleration, and speed, enhancing driver or operator confidence and maneuverability. Drivelines with features like traction control systems, limited-slip differentials, or electronic stability control provide additional safety measures by improving traction, stability, and handling in challenging road or operating conditions. By ensuring optimal power distribution and control, drivelines enhance the overall safety and stability of vehicles and equipment.
7. Durability and Reliability: Drivelines are built to withstand harsh operating conditions and provide long-term durability and reliability. They are engineered with high-quality materials, precise manufacturing processes, and advanced technologies to ensure the driveline components can endure the stresses of power transmission. Well-designed drivelines require minimal maintenance, reducing downtime and enhancing the overall reliability of vehicles and equipment.
8. Specialized Functionality: Drivelines offer specialized functionality for specific types of vehicles and equipment. For example, in off-road vehicles or heavy-duty construction equipment, drivelines with features like differential locks, torque vectoring, or adjustable suspension systems provide enhanced traction, stability, and control. In agricultural machinery, drivelines with power take-off (PTO) units enable the connection of various implements for specific tasks like plowing, seeding, or harvesting. Such specialized driveline features enhance the performance and versatility of vehicles and equipment in their respective applications.
In summary, drivelines provide numerous benefits for different types of vehicles and equipment. They ensure efficient power transmission, facilitate mobility and maneuverability, offer versatility and adaptability, contribute to efficiency and fuel economy, handle heavy loads, enhance safety and control, provide durability and reliability, and offer specialized functionality. By incorporating well-designed drivelines, manufacturers can optimize the performance, productivity, and overall functionality of vehicles and equipment across various industries.


editor by CX 2024-04-16
China Custom Drive Gear Pto and Transmission Shaft Factory Steel Precision Agricultural Machinery Use Power Transmission Shaft Transmission Shaft Factory Steel Precision45 PTO Driveline
Product Description
Company Profile
HangZhou Xihu (West Lake) Dis. East Port Gear Manufacturing factory is located in Zhoujia Industrial Zone, CHINAMFG Town, HangZhou, 3km away from Xihu (West Lake) Dis.qian Lake. It focuses on precision gear research, development, production and sales. The factory has obtained ISO9001: 2015 certificate, IATF16949:2016. The main export markets were North America, South America and Europe. Products can be customized and mainly includes: New Energy Motor Shaft, Oil Pump Gear, Agricultural Machinery Gear, Transmission Gear, Electric Vehicle gear, etc. We are sincerely willing to cooperate with enterprises from all over the world.
Equipment And Main Products
Certifications
FAQ
Q1:How is the quality of your product?
A:Our product has reliable quality, high wear life
Q2:Customization process/work flow?
Advisory – Material selection – 2D/3D Drawing – Quotation – Payment – Production – Quality Control – Package – Delivery
Q3: What is your terms of packing?
A:Generally, we pack our goods in wooden cases, If you have special request about packing, pls negotiate with us in advance, we can pack the goods as your request.
Q4:Price?
A:We will offer competitive price after receiving your drawing
Q5:What is your terms of payment?
A:30% T/T advanced, 70% T/T before shipping
Q6:What is your terms of delivery?
A: FOB
Q7:What drawing software does your company use?
A:CAXA
Q8:Do you test all your goods before delivery?
A: Yes, we have 100% test before delivery
Q9:How about your delivery time?
A:Product can often be delivered within 40-90 days
Q10:Sample?
A:We offer paid sample.If you have sample requirements, please feel free to contact us at any time
Q11:What logistics packaging does your company use?
A:Express for urgent orders. UPS, FedEx, DHL, TNT, EMS.
Q12:Application range?
A:Automotive, medical, automation, agricultural, marine, etc.
Q13: How do you make our business long-term and good relationship?
A:1. We keep good quality and competitive price to ensure our customers benefit ;
2. We respect every customer as our friend and we sincerely do business and make friends with them,
no matter where they come from.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Motor, Electric Cars, Motorcycle, Machinery, Agricultural Machinery, Car |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Samples: |
US$ 50/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample 40000
|
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

What factors should be considered when selecting the appropriate PTO driveline for an application?
When selecting the appropriate PTO (Power Take-Off) driveline for an application, several factors need to be considered to ensure optimal performance, efficiency, and safety. Here are some key factors to take into account:
1. Power Requirements:
– Determine the power requirements of the driven equipment. Consider the horsepower (HP) or kilowatt (kW) rating necessary to operate the equipment effectively. The PTO driveline should be capable of transmitting the required power without overloading or damaging the driveline components.
2. Speed and RPM:
– Identify the desired operating speed and RPM (Rotations Per Minute) of the driven equipment. The PTO driveline should be compatible with the required speed range to ensure efficient power transmission. Consider the maximum and minimum RPM ratings of the driveline and select one that matches the specific speed requirements of the application.
3. Torque Requirements:
– Determine the torque requirements of the driven equipment. Torque is the rotational force required to perform the intended task. Consider both the maximum and average torque demands during operation. Ensure that the selected PTO driveline can handle the torque levels without exceeding its maximum torque capacity or causing premature wear or failure.
4. Application Type:
– Consider the specific application and the type of equipment involved. Different applications may require different PTO driveline designs and features. For example, agricultural equipment such as mowers, balers, or tillers may benefit from a constant velocity (CV) PTO driveline to accommodate varying angles and speeds, while stationary equipment like generators or water pumps may use a non-constant velocity (non-CV) PTO driveline.
5. Safety Considerations:
– Evaluate the safety requirements of the application. Certain applications may require additional safety features such as shear bolts or slip clutches to protect against excessive loads, sudden obstructions, or torque spikes. Ensure that the selected PTO driveline incorporates the necessary safety mechanisms to prevent damage to the driveline and equipment, as well as to ensure the safety of operators and bystanders.
6. Durability and Maintenance:
– Consider the durability and maintenance requirements of the PTO driveline. Evaluate the quality and reliability of the driveline components, such as bearings, joints, and couplings. Choose a driveline that is built to withstand the demands of the application and requires minimal maintenance to ensure long-term performance and reduce downtime.
7. Compatibility:
– Ensure compatibility between the PTO driveline and the power source (e.g., tractor, engine). Consider the PTO driveline’s connection type, size (e.g., spline count, shaft diameter), and mounting configuration to ensure a proper fit and connection with the power source.
8. Environmental Conditions:
– Take into account the environmental conditions in which the PTO driveline will operate. Factors such as temperature extremes, exposure to moisture, dust, or chemicals can impact the driveline’s performance and longevity. Choose a driveline that is designed to withstand the specific environmental conditions of the application.
9. Manufacturer and Quality:
– Consider the reputation and reliability of the PTO driveline manufacturer. Opt for reputable manufacturers known for producing high-quality and durable driveline systems. Research customer reviews and seek recommendations from industry experts to ensure you choose a reliable and reputable brand.
By carefully considering these factors, you can select the most appropriate PTO driveline for your specific application. It is recommended to consult with manufacturers, industry experts, or equipment dealers to get further guidance and ensure the right driveline selection for your needs.

How do PTO drivelines enhance the performance of tractors and agricultural equipment?
PTO (Power Take-Off) drivelines play a crucial role in enhancing the performance of tractors and agricultural equipment. By providing a reliable and versatile power source, PTO drivelines improve the functionality, efficiency, and productivity of agricultural machinery. Here are several ways in which PTO drivelines enhance the performance of tractors and agricultural equipment:
1. Power Versatility:
– PTO drivelines enable tractors and agricultural equipment to utilize a wide range of power-driven implements and attachments. By connecting to the PTO shaft of a tractor, implements such as mowers, tillers, seeders, and balers can be powered directly, eliminating the need for separate engines or motors. This versatility allows farmers to perform multiple tasks using a single power source, reducing equipment redundancy and increasing operational efficiency.
2. Increased Efficiency:
– PTO drivelines contribute to increased efficiency by providing a direct power transfer mechanism. The driveline ensures minimal power loss during transmission, resulting in more efficient utilization of available power. This efficiency leads to improved performance and reduced fuel consumption, ultimately optimizing resource utilization and lowering operating costs.
3. Flexibility in Equipment Usage:
– PTO drivelines offer flexibility in equipment usage by allowing quick and easy attachment and detachment of implements. Farmers can rapidly switch between different implements, tailoring the equipment to suit specific tasks and field conditions. This flexibility enhances productivity as it reduces downtime associated with changing equipment, enabling farmers to adapt to changing agricultural needs efficiently.
4. Time Savings:
– PTO drivelines contribute to time savings by enabling faster and more efficient completion of agricultural tasks. Machinery powered by PTO drivelines can operate at higher speeds and cover larger areas, reducing the time required for tasks such as mowing, tilling, planting, and harvesting. Additionally, the direct power transfer provided by PTO drivelines eliminates the need for manual labor or slower power transmission methods, further enhancing productivity and time efficiency.
5. Enhanced Capability:
– PTO drivelines enhance the capability of tractors and agricultural equipment by enabling them to handle a broader range of tasks and operate specialized implements. For example, PTO-driven sprayers allow precise and efficient spraying of fertilizers and pesticides, ensuring optimal crop health. PTO-driven balers enable efficient baling and packaging of hay or other forage materials. The versatility and enhanced capability provided by PTO drivelines allow farmers to expand their operations and achieve higher levels of productivity.
6. Consistent Power Delivery:
– PTO drivelines ensure consistent power delivery to agricultural equipment, resulting in consistent and uniform operation. The power from the tractor or power source is transmitted directly to the driven machinery, maintaining a steady power input. Consistent power delivery helps ensure optimum performance, reducing variations in output quality and minimizing the need for rework or adjustments.
7. Improved Safety:
– PTO drivelines contribute to improved safety by reducing the need for direct operator interaction with moving parts. Implements and machinery powered by PTO drivelines often have guards and safety features in place to protect operators from potential hazards. Additionally, the direct power transfer eliminates the need for manual belt or chain drives, reducing the risk of entanglement or mechanical failures.
8. Advanced Technology Integration:
– PTO drivelines enable the integration of advanced technologies and features into agricultural equipment. For example, PTO-driven machinery can incorporate precision farming technologies, such as GPS guidance systems, automatic controls, and variable-rate application capabilities. These technologies enhance accuracy, efficiency, and input optimization, resulting in improved performance and increased yields.
Overall, PTO drivelines significantly enhance the performance of tractors and agricultural equipment by providing a versatile power source, increasing efficiency, enabling flexibility in equipment usage, saving time, enhancing capability, ensuring consistent power delivery, improving safety, and facilitating the integration of advanced technologies. These advantages contribute to increased productivity, improved operational effectiveness, and enhanced profitability in agricultural operations.

What is a PTO driveline and how does it function in agricultural and industrial machinery?
A PTO (Power Take-Off) driveline is a mechanical system used in agricultural and industrial machinery to transfer power from a power source, such as an engine or motor, to driven equipment or implements. It consists of several components that work together to transmit power efficiently and reliably. Let’s explore the key elements of a PTO driveline and how it functions in agricultural and industrial machinery:
1. Power Source:
The power source in a PTO driveline is typically an engine or motor, such as the one found in a tractor or industrial machine. It generates rotational power, which serves as the energy source for the entire system.
2. PTO Shaft:
The PTO shaft is a rotating shaft that extends from the power source to the driven equipment. It is designed to transmit power from the power source to the implement. The PTO shaft is connected to the power source at one end and to the driven equipment at the other end.
3. PTO Clutch:
The PTO clutch is a mechanism that allows the operator to engage or disengage the power transfer between the power source and the driven equipment. It is usually controlled by a lever or switch, enabling the operator to start or stop the power transmission as needed. The PTO clutch ensures that power is only transferred when required, providing control and safety during operation.
4. PTO Gearbox:
In some machinery, a PTO gearbox is used to adjust the speed and torque of the power transfer. The gearbox is situated between the power source and the PTO shaft. It contains a set of gears that can be switched or adjusted to modify the rotational speed and torque of the PTO shaft. This allows for the adaptation of power to suit different implements or tasks.
5. PTO Driven Equipment:
The driven equipment refers to the implements or machinery that receive power from the PTO driveline. In agricultural machinery, this can include equipment like plows, mowers, balers, seeders, and grain augers. In industrial machinery, it can involve devices such as pumps, generators, compressors, or conveyor systems. The PTO driveline provides the necessary power to drive these equipment and enable their intended functions.
Function in Agricultural Machinery:
In agricultural machinery, the PTO driveline plays a crucial role in powering various implements and equipment. When the PTO clutch is engaged, rotational power is transmitted from the tractor’s engine to the PTO shaft. The PTO shaft, in turn, transfers this power to the driven equipment, allowing it to perform its task. For example, a PTO-driven mower receives power through the PTO shaft, enabling it to rotate the cutting blades and mow the field. The PTO driveline provides a flexible and efficient means of powering agricultural implements, contributing to increased productivity and versatility in farming operations.
Function in Industrial Machinery:
In industrial machinery, the PTO driveline serves a similar purpose by transferring power from the main power source to various driven equipment. The PTO clutch is engaged to initiate power transfer, and the PTO shaft transmits rotational power to the driven equipment. This allows the equipment to perform its specific function. For example, in a pump application, the PTO driveline powers the pump, enabling it to generate fluid flow or pressure. In a conveyor system, the PTO driveline drives the conveyor belt, facilitating material transportation. The PTO driveline in industrial machinery ensures efficient power transmission, enabling the equipment to operate effectively in industrial settings.
Overall, the PTO driveline is a critical component in agricultural and industrial machinery, facilitating the transfer of power from a power source to driven equipment. By utilizing the PTO shaft, clutch, gearbox (if present), and other components, the PTO driveline provides a reliable and efficient means of power transmission, enhancing the functionality and performance of machinery in these sectors.


editor by CX 2024-04-15
China Custom Transmission Shaft for Agricultural Machinery St52 E355 Q215b 45 # 1045 40cr 5140 1.7035 40mnb Pto Shaft-2 Precision Shaped Steel Pipe PTO Driveline
Product Description
Introduce
Specially shaped seamless steel pipes include those with non circular cross-sectional profiles, those with equal wall thickness, those with variable wall thickness, those with variable diameter and wall thickness along the length direction, and those with symmetrical and asymmetric cross-sectional profiles. Such as square, rectangular, conical, trapezoidal, spiral, etc. Specially shaped steel pipes are more suitable for the unique usage conditions, saving metal and improving labor productivity in component manufacturing. It is widely used in aviation, automobiles, shipbuilding, mining machinery, agricultural machinery, construction, light textile, and boiler manufacturing. The methods for producing shaped pipes include cold drawing, electric welding, extrusion, hot rolling, etc. Among them, the cold drawing method has been widely used.
Product Parameters
| Triangle Steel Tube | Outer (mm) | Inner (mm) | ||
| H | S | H | S | |
| 1S | 32.4 | 2.5 | 26.6 | 3.5 |
| 2S | 36.1 | 3.4 | 29 | 4 |
| 4S | 43.4 | 3.3 | 36.1 | 4.4 |
| 5S | 51.3 | 2.9 | 44.7 | 4 |
| 6S | 53.6 | 3.8 | 44.7 | 4 |
| 7S | 53.6 | 3.8 | 44.7 | 5.5 |
| 8S | 62.7 | 4 | 53.6 | 4.5 |
| 9S | 62.7 | 4 | 53.6 | 5.5 |
Chemical composition
| st52 | C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Ni | Cu | Mo |
| Q215B | 0.37-0.44 | 0.17-0.37 | 0.5-0.8 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.035 | 0.8-1.1 | ≤0.3 | ≤0.3 | ≤0.15 |
| 45#/1045 | 0.43-0.5 | – | 0.6-0.9 | ≤0.04 | ≤0.05 | – | – | – | — |
| 40Cr/5140/1.7035 | 0.37-0.44 | 0.17-0.37 | 0.5-0.8 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.035 | 0.8-1.1 | ≤0.3 | ≤0.3 | ≤0.15 |
| 40MnB | 0.37-0.44 | 0.17-0.37 | 1.1-1.4 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.035 | ≤0.3 | ≤0.3 | ≤0.3 | ≤0.15 |
Product Description
| Production Range | Outer Diameter:6-530mm (0.24 inch – 21.18 inch) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wall Thickness:0.8-2 tons of inventory goods and a number of long-term stable cooperative customers.
5. What services can we provide? 6. How can we get your price? /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
What maintenance practices are crucial for extending the lifespan of PTO driveline components?Proper maintenance is essential for extending the lifespan of PTO (Power Take-Off) driveline components and ensuring their optimal performance. By following these crucial maintenance practices, you can minimize wear and tear, prevent premature failures, and maximize the longevity of your PTO driveline: 1. Regular Inspection: – Conduct regular visual inspections of the entire PTO driveline assembly. Look for signs of damage, wear, or loose components. Pay close attention to the driveline shaft, universal joints, bearings, and couplings. Detecting early signs of wear or damage allows for timely repairs or replacements, preventing further damage and ensuring the longevity of the driveline components. 2. Lubrication: – Proper lubrication is crucial for the smooth operation and longevity of PTO driveline components. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for lubricating the driveline, including the type of lubricant and the recommended intervals. Ensure that all lubrication points, such as universal joints and bearings, receive adequate grease or oil. Regular lubrication minimizes friction, reduces wear, and helps maintain the driveline’s efficiency and reliability. 3. Tightening and Fastener Checks: – Periodically check and tighten all fasteners, such as bolts, nuts, and set screws, within the PTO driveline assembly. Vibrations and continuous operation can cause these fasteners to loosen over time, potentially leading to misalignment or damage. Regularly inspecting and tightening the fasteners ensures that the driveline remains securely connected, reducing the risk of component failure or disengagement during operation. 4. Balance and Alignment: – Proper balance and alignment of the PTO driveline components are crucial for reducing vibrations, minimizing stress, and extending component life. Inspect and correct any imbalances or misalignments in the driveline components, including the driveline shaft and universal joints. Imbalances or misalignments can cause excessive wear on bearings, joints, and other driveline parts. Addressing these issues through proper balancing and alignment ensures smoother operation and prolongs the lifespan of the driveline. 5. Protection from Contaminants: – Protecting the PTO driveline components from contaminants, such as dirt, debris, and moisture, is essential for preventing corrosion, premature wear, and damage. Clean the driveline regularly, removing any accumulated dirt or debris. Consider using protective covers or shields to minimize exposure to moisture and other environmental elements. Additionally, store the driveline in a clean and dry environment when not in use. Keeping the driveline components clean and protected helps maintain their performance and extends their lifespan. 6. Proper Usage and Handling: – Follow the recommended usage guidelines provided by the manufacturer to ensure the driveline components are not subjected to excessive loads, speeds, or angles beyond their design capabilities. Avoid overloading the driveline or using it with incompatible equipment. Properly engage and disengage the PTO driveline according to the manufacturer’s instructions to prevent abrupt shocks or excessive wear. Handling the driveline with care and following proper usage practices reduces stress on the components and contributes to their longevity. 7. Prompt Repairs: – Address any signs of damage, wear, or malfunction promptly. If you notice unusual vibrations, noise, or any other abnormal behavior during operation, investigate and address the issue as soon as possible. Delaying repairs or ignoring potential problems can lead to further damage and more extensive repairs down the line. Timely repairs help prevent component failures and extend the overall lifespan of the PTO driveline. 8. Professional Maintenance: – For more complex maintenance tasks or when in doubt, consider seeking professional assistance. Experienced technicians or authorized service centers can provide thorough inspections, perform specialized maintenance procedures, and offer expert advice on maintaining the PTO driveline components. Professional maintenance ensures that the driveline receives the necessary care and attention to maximize its lifespan and performance. By implementing these crucial maintenance practices, you can significantly extend the lifespan of PTO driveline components. Regular inspections, proper lubrication, tightening and fastener checks, balance and alignment, protection from contaminants, proper usage and handling, prompt repairs, and seeking professional maintenance when needed are key to preserving the driveline’s longevity and optimizing its performance.
Are there any limitations or challenges associated with using PTO driveline systems?While PTO (Power Take-Off) driveline systems offer numerous benefits, there are also certain limitations and challenges associated with their use. Here are some of the key considerations: 1. Safety Risks: – PTO driveline systems can pose safety risks if not handled properly. The rotating components of the driveline, such as the shafts, yokes, and universal joints, can cause serious injuries if operators come into contact with them while in motion. It is crucial to follow proper safety procedures, including the use of shields, guards, and safety devices, to prevent accidents. Adequate training and awareness about the potential hazards associated with PTO driveline systems are essential. 2. Maintenance and Lubrication: – PTO driveline systems require regular maintenance and lubrication to ensure optimal performance and longevity. The universal joints, splines, and other moving parts need to be inspected, cleaned, and properly lubricated according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Neglecting maintenance can lead to premature wear, increased friction, and potential failures, compromising the driveline’s efficiency and reliability. 3. Alignment and Misalignment: – Proper alignment between the power source and the driven equipment is crucial for efficient power transfer in PTO driveline systems. Misalignment can result in increased vibration, excessive wear, and reduced power transmission efficiency. Achieving and maintaining proper alignment can be challenging, especially when connecting the driveline to equipment with varying mounting heights, angles, or misaligned driveline components. Operators need to carefully align the driveline to minimize stress and ensure smooth operation. 4. Length and Compatibility: – PTO driveline systems need to be appropriately sized and compatible with the specific equipment and applications they are intended for. Variations in length, connection types, and torque requirements among different equipment can pose challenges in selecting the right driveline. Ensuring proper compatibility and fit between the driveline and the equipment is crucial for optimal power transmission and safety. Customization or adaptation may be necessary in certain cases, which could add complexity and cost. 5. Torque Overload and Protection: – PTO driveline systems are susceptible to torque overload, especially when the driven equipment encounters sudden resistance or obstructions. Excessive torque can lead to driveline component failures, such as universal joint breakage or shear pin failure, potentially causing damage to the driveline or other connected components. Proper protection mechanisms, such as shear pins, slip clutches, or overload clutches, should be employed to prevent damage and ensure operator safety. 6. Noise and Vibration: – PTO driveline systems can generate significant noise and vibration during operation. The rotating components, imbalances, misalignments, or worn-out components can contribute to increased noise levels and vibration. Excessive noise and vibration not only affect operator comfort but can also lead to component fatigue and premature wear. Employing appropriate vibration dampening techniques, balancing the driveline components, and using vibration-absorbing materials can help mitigate these issues. 7. Environmental Factors: – PTO driveline systems may be exposed to various environmental factors, such as dust, debris, moisture, and temperature extremes. These factors can impact the driveline’s performance and longevity. Dust and debris can accumulate in the driveline components, leading to increased friction and wear. Moisture and corrosive environments can cause rust and degradation of driveline parts. Extreme temperatures can affect the lubrication properties and material integrity. Regular inspection, cleaning, and appropriate protection measures are essential to mitigate the impact of environmental factors. In summary, while PTO driveline systems offer significant advantages, there are limitations and challenges that need to be addressed for safe and efficient operation. These include safety risks, maintenance requirements, alignment considerations, compatibility issues, torque overload protection, noise and vibration management, and the impact of environmental factors. By understanding and addressing these challenges, operators can ensure the proper functioning and longevity of PTO driveline systems.
Which industries and applications commonly utilize PTO drivelines for power distribution?PTO (Power Take-Off) drivelines are widely used in various industries and applications that require the distribution of rotational power from a power source to driven equipment. The versatility and efficiency of PTO drivelines make them suitable for a range of tasks across different sectors. Let’s explore some of the industries and applications that commonly utilize PTO drivelines: 1. Agriculture: The agriculture industry extensively relies on PTO drivelines for power distribution. Tractors equipped with PTO drivelines are commonly used to operate a wide array of implements and machinery, such as mowers, balers, harvesters, sprayers, seeders, and spreaders. PTO drivelines enable efficient power transmission for tasks like cutting, baling, spraying, planting, and spreading, contributing to the overall productivity and effectiveness of agricultural operations. 2. Construction and Earthmoving: In the construction and earthmoving industry, PTO drivelines are utilized in heavy machinery for tasks such as excavating, grading, and material handling. Equipment like backhoes, loaders, and skid-steer loaders may feature PTO drivelines to power attachments like augers, trenchers, and hydraulic hammers. This enables these machines to perform a variety of functions efficiently, enhancing productivity on construction sites. 3. Forestry: Forestry operations often employ PTO drivelines for power distribution in equipment used for wood processing, chipping, and mulching. Forestry mulchers, wood chippers, and stump grinders are commonly driven by PTO drivelines, allowing them to convert trees and wood waste into manageable sizes or mulch. PTO drivelines provide the necessary power to these machines, enabling efficient and effective forestry operations. 4. Landscaping and Groundskeeping: The landscaping and groundskeeping industry extensively uses PTO drivelines for power distribution in equipment like lawn mowers, rotary cutters, and turf aerators. PTO-powered mowers can cover large areas efficiently, while rotary cutters are used for clearing brush and rough vegetation. Turf aerators equipped with PTO drivelines help maintain healthy lawns by improving soil aeration. PTO drivelines contribute to the performance and productivity of landscaping and groundskeeping tasks. 5. Utility and Municipal Services: PTO drivelines find applications in utility and municipal services, where various equipment is used for maintenance and operations. Street sweepers, snow blowers, salt spreaders, and sewer cleaners often rely on PTO drivelines for power distribution. These machines can efficiently perform their respective tasks, such as cleaning streets, removing snow, spreading de-icing material, and maintaining sewer systems. 6. Industrial and Manufacturing: In the industrial and manufacturing sectors, PTO drivelines are utilized in machinery and equipment for power distribution. Industrial mixers, pumps, generators, and compressors often incorporate PTO drivelines to transfer rotational power efficiently. This enables these machines to perform their specific functions, such as mixing materials, pumping fluids, generating electricity, or compressing air. These are just a few examples of the industries and applications that commonly utilize PTO drivelines for power distribution. The versatility and efficiency of PTO drivelines make them suitable for a wide range of tasks, enabling power to be harnessed from a power source and efficiently distributed to driven equipment. PTO drivelines significantly contribute to the productivity and functionality of machinery in various sectors, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
China Good quality Precision Transmission /Drive/Axle/Auto/Spline/Machinery Parts/ Rotor Gear Customized Machining Knurling Shaft Drive LineProduct Description
Precision Shaft by CNC Turning Machining Our advantage: *Specialization in CNC formulations of high precision and quality Production machine: Inspection equipment : Certificate:
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
What factors should be considered when designing an efficient driveline system?Designing an efficient driveline system involves considering various factors that contribute to performance, reliability, and overall system efficiency. Here are the key factors that should be considered when designing an efficient driveline system: 1. Power Requirements: The power requirements of the vehicle play a crucial role in designing an efficient driveline system. It is essential to determine the maximum power output of the engine and ensure that the driveline components can handle and transfer that power efficiently. Optimizing the driveline for the specific power requirements helps minimize energy losses and maximize overall efficiency. 2. Weight and Packaging: The weight and packaging of the driveline components have a significant impact on system efficiency. Lightweight materials and compact design help reduce the overall weight of the driveline, which can improve fuel efficiency and vehicle performance. Additionally, efficient packaging ensures that driveline components are properly integrated, minimizing energy losses and maximizing available space within the vehicle. 3. Friction and Mechanical Losses: Minimizing friction and mechanical losses within the driveline system is crucial for achieving high efficiency. Frictional losses occur at various points, such as bearings, gears, and joints. Selecting low-friction materials, optimizing lubrication systems, and implementing efficient bearing designs can help reduce these losses. Additionally, employing advanced gear designs, such as helical or hypoid gears, can improve gear mesh efficiency and reduce power losses. 4. Gear Ratios and Transmission Efficiency: The selection of appropriate gear ratios and optimizing transmission efficiency greatly impacts driveline efficiency. Gear ratios should be chosen to match the vehicle’s power requirements, driving conditions, and desired performance characteristics. In addition, improving the efficiency of the transmission, such as reducing gear mesh losses and enhancing hydraulic or electronic control systems, can contribute to overall driveline efficiency. 5. Aerodynamic Considerations: Aerodynamics play a significant role in a vehicle’s overall efficiency, including the driveline system. Reducing aerodynamic drag through streamlined vehicle design, efficient cooling systems, and appropriate underbody airflow management can enhance driveline efficiency by reducing the power required to overcome air resistance. 6. System Integration and Control: Efficient driveline design involves seamless integration and control of various components. Employing advanced control systems, such as electronic control units (ECUs), can optimize driveline operation by adjusting power distribution, managing gear shifts, and optimizing torque delivery based on real-time driving conditions. Effective system integration ensures smooth communication and coordination between driveline components, improving overall efficiency. 7. Environmental Considerations: Environmental factors should also be taken into account when designing an efficient driveline system. Considerations such as emissions regulations, sustainability goals, and the use of alternative power sources (e.g., hybrid or electric drivetrains) can influence driveline design decisions. Incorporating technologies like regenerative braking or start-stop systems can further enhance efficiency and reduce environmental impact. 8. Reliability and Durability: Designing an efficient driveline system involves ensuring long-term reliability and durability. Selecting high-quality materials, performing thorough testing and validation, and considering factors such as thermal management and component durability help ensure that the driveline system operates efficiently over its lifespan. By considering these factors during the design process, engineers can develop driveline systems that are optimized for efficiency, performance, and reliability, resulting in improved fuel economy, reduced emissions, and enhanced overall vehicle efficiency.
How do drivelines enhance the performance of different types of vehicles?Drivelines significantly contribute to enhancing the performance of different types of vehicles by optimizing power delivery, improving traction, and tailoring the driving characteristics to suit specific needs. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drivelines enhance performance in various vehicle types: 1. Passenger Cars: In passenger cars, driveline configurations, such as front-wheel drive (FWD), rear-wheel drive (RWD), and all-wheel drive (AWD), play a crucial role in performance. Here’s how drivelines enhance performance in passenger cars:
2. Sports Cars and Performance Vehicles: Driveline systems in sports cars and performance vehicles are designed to enhance acceleration, handling, and overall driving dynamics. Key features include:
3. Off-Road Vehicles: Drivelines in off-road vehicles are designed to provide exceptional traction, durability, and maneuverability in challenging terrains. Key features include:
4. Trucks and Commercial Vehicles: Drivelines in trucks and commercial vehicles are engineered to provide high torque delivery, durability, and efficiency. Key features include:
5. Electric and Hybrid Vehicles: Drivelines in electric and hybrid vehicles play a crucial role in delivering power from the electric motor(s) to the wheels. Key features include:
These are just a few examples of how drivelines enhance the performance of different types of vehicles. Driveline configurations, technologies, and engineering considerations are tailored to each vehicle type, optimizing power delivery, handling, traction, and other performance characteristics specific to their intended use and market segment.
Can you explain the components of a typical driveline and their specific roles?A typical driveline consists of several components that work together to transmit power from the engine or power source to the driven components, enabling motion and providing torque. Each component plays a specific role in the driveline system. Here’s an explanation of the key components of a typical driveline and their specific roles: 1. Engine: The engine is the power source of the driveline system. It converts fuel energy (such as gasoline or diesel) into mechanical power by the process of combustion. The engine generates rotational power, which is transferred to the driveline to initiate power transmission. 2. Transmission: The transmission is responsible for selecting the appropriate gear ratio and transmitting power from the engine to the driven components. It allows the driver or operator to control the speed and torque output of the driveline. In manual transmissions, the driver manually selects the gears, while in automatic transmissions, the gear shifts are controlled by the vehicle’s computer system. 3. Drive Shaft: The drive shaft, also known as a propeller shaft or prop shaft, is a tubular component that transmits rotational power from the transmission to the differential or the driven components. It typically consists of a hollow metal tube with universal joints at both ends to accommodate variations in driveline angles and allow for smooth power transfer. 4. Differential: The differential is a gearbox-like component that distributes power from the drive shaft to the wheels or driven axles while allowing them to rotate at different speeds, particularly during turns. It compensates for the difference in rotational speed between the inner and outer wheels in a turn, ensuring smooth and controlled operation of the driveline system. 5. Axles: Axles are shafts that connect the differential to the wheels. They transmit power from the differential to the wheels, allowing them to rotate and generate motion. In vehicles with independent suspension, each wheel typically has its own axle, while in solid axle configurations, a single axle connects both wheels on an axle assembly. 6. Clutch: In manual transmission systems, a clutch is employed to engage or disengage the engine’s power from the driveline. It allows the driver to smoothly engage the engine’s power to the transmission when shifting gears or coming to a stop. By disengaging the clutch, power transmission to the driveline is temporarily interrupted, enabling gear changes or vehicle stationary positions. 7. Torque Converter: Torque converters are used in automatic transmissions to transfer power from the engine to the transmission. They provide a fluid coupling between the engine and transmission, allowing for smooth power transmission and torque multiplication. The torque converter also provides a torque amplification effect, which helps in vehicle acceleration. 8. Universal Joints: Universal joints, also known as U-joints, are flexible couplings used in the driveline to accommodate variations in angles and misalignments between the components. They allow for the smooth transmission of power between the drive shaft and other components, compensating for changes in driveline angles during vehicle operation or suspension movement. 9. Constant Velocity Joints (CV Joints): CV joints are specialized joints used in some drivelines, particularly in front-wheel-drive and all-wheel-drive vehicles. They enable smooth power transmission while accommodating variations in angles and allowing the wheels to turn at different speeds. CV joints maintain a constant velocity during rotation, minimizing vibrations and power losses. 10. Transfer Case: A transfer case is a component found in four-wheel-drive and all-wheel-drive systems. It transfers power from the transmission to both the front and rear axles, allowing all wheels to receive power. The transfer case usually includes additional components such as a multi-speed gearbox and differential mechanisms to distribute power effectively to the axles. These are the key components of a typical driveline and their specific roles. Each component is crucial in transferring power, enabling motion, and ensuring the smooth and efficient operation of vehicles and equipment.
China supplier Customized High Precision Spare Parts Auto/Truck/Drive/Gear/Spline/Propeller/Half/Sleeve/Machinery/Sliding/Transmission Axle Shaft 42CrMo 20crmoti Drive LineProduct Description
Customized High Precision Spare Parts Auto/Truck/Drive/Gear/Spline/Propeller/Half/Sleeve/Machinery/Sliding/Transmission Axle Shaft 42CrMo 20CrMoTi
(1) Accessory products of the truck, the product quality is stable and reliable.
Factory Show More Products
Function Heavy trucks usually have double rear axles. If they are driven separately, they need to use 2 transmission shafts or add a transfer case at the output of the gearbox, which is heavy and cumbersome. Now a through shaft is designed in the middle axle to solve this problem. Only 1 transmission shaft is needed to drive 2 rear axles at the same time. Packaging & Shipping Exhibition FAQ Q1. Are you a factory or trading company? Q2. What are the advantages of your products? Q3. How about products price? Q4. What is your terms of packing? Q5. How to guarantee your after-sales service? Certifications /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
How do drivelines handle variations in load and torque during operation?Drivelines are designed to handle variations in load and torque during operation by incorporating various components and mechanisms that optimize power transmission and mitigate the effects of these variations. Let’s delve into the ways drivelines handle load and torque variations: 1. Flexible Couplings: Drivelines often utilize flexible couplings, such as universal joints or constant velocity (CV) joints, to accommodate misalignment and angular variations between connected components. These couplings allow for smooth power transmission even when there are slight misalignments or changes in angles. They can compensate for variations in load and torque by flexing and adjusting their angles, thereby reducing stress on the driveline components. 2. Torque Converters: In some driveline systems, such as those found in automatic transmissions, torque converters are employed. Torque converters use hydraulic principles to transmit power between the engine and the drivetrain. They provide a degree of slip, which allows for torque multiplication and smooth power delivery, especially during low-speed and high-load conditions. Torque converters help manage variations in torque by absorbing and dampening sudden changes, ensuring smoother operation. 3. Clutches: Clutches play a critical role in drivelines, particularly in manual transmissions or systems that require torque control. Clutches engage and disengage the power flow between the engine and the drivetrain. By engaging or disengaging the clutch, the driveline can handle variations in load and torque. For instance, when starting a vehicle from a standstill, the clutch gradually engages to transmit power smoothly and prevent abrupt torque surges. 4. Gearboxes and Transmission Systems: Drivelines often incorporate gearboxes and transmissions that provide multiple gear ratios. These systems allow for varying torque and speed outputs, enabling the driveline to adapt to different load conditions. By changing gears, the driveline can match the power requirements of the vehicle or machinery to the load and torque demands, optimizing power delivery and efficiency. 5. Differential Systems: In drivelines for vehicles with multiple driven wheels, such as cars with rear-wheel drive or all-wheel drive, differential systems are employed. Differentials distribute torque between the driven wheels while allowing them to rotate at different speeds, particularly during turns. This capability helps handle variations in load and torque between the wheels, ensuring smooth operation and minimizing tire wear. 6. Control Systems: Modern drivelines often incorporate control systems that monitor and adjust power distribution based on various inputs, including load and torque conditions. These control systems, such as electronic control units (ECUs), can optimize power delivery, manage gear shifts, and adjust torque output to handle variations in load and torque. They may also incorporate sensors and feedback mechanisms to continuously monitor driveline performance and make real-time adjustments. 7. Overload Protection Mechanisms: Some driveline systems include overload protection mechanisms to safeguard against excessive load or torque. These mechanisms can include torque limiters, shear pins, or safety clutches that disengage or slip when the load or torque exceeds a certain threshold. By providing a fail-safe mechanism, drivelines can protect the components from damage due to sudden or excessive variations in load and torque. By incorporating these components and mechanisms, drivelines are capable of handling variations in load and torque during operation. They optimize power transmission, ensure smooth operation, and protect the driveline components from excessive stress or damage, ultimately enhancing the performance and longevity of the driveline system.
Are there any limitations or disadvantages associated with driveline systems?While driveline systems offer numerous advantages in terms of power transmission and vehicle performance, there are also some limitations and disadvantages associated with their use. It’s important to consider these factors when designing, operating, and maintaining driveline systems. Let’s explore some of the limitations and disadvantages: 1. Complex Design and Integration: Driveline systems can be complex in design, especially in modern vehicles with advanced technologies. They often consist of multiple components, such as transmissions, differentials, transfer cases, and drive shafts, which need to be properly integrated and synchronized. The complexity of the driveline system can increase manufacturing and assembly challenges, as well as the potential for compatibility issues or failures if not designed and integrated correctly. 2. Energy Losses: Driveline systems can experience energy losses during power transmission. These losses occur due to factors such as friction, heat generation, mechanical inefficiencies, and fluid drag in components like gearboxes, differentials, and torque converters. The energy losses can negatively impact overall efficiency and result in reduced fuel economy or power output, especially in systems with multiple driveline components. 3. Limited Service Life and Maintenance Requirements: Driveline components, like any mechanical system, have a limited service life and require regular maintenance. Components such as clutches, bearings, gears, and drive shafts are subject to wear and tear, and may need to be replaced or repaired over time. Regular maintenance, including lubrication, adjustments, and inspections, is necessary to ensure optimal performance and prevent premature failures. Failure to perform proper maintenance can lead to driveline malfunctions, increased downtime, and costly repairs. 4. Weight and Space Constraints: Driveline systems add weight and occupy space within a vehicle. The additional weight affects fuel efficiency and overall vehicle performance. Moreover, the space occupied by driveline components can limit design flexibility, particularly in compact or electric vehicles where space optimization is crucial. Manufacturers must strike a balance between driveline performance, vehicle weight, and available space to meet the requirements of each specific vehicle type. 5. Noise, Vibration, and Harshness (NVH): Driveline systems can generate noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH) during operation. Factors such as gear meshing, unbalanced rotating components, or improper driveline alignment can contribute to unwanted vibrations or noise. NVH issues can affect driving comfort, passenger experience, and vehicle refinement. Manufacturers employ various techniques, including vibration dampening materials, isolators, and precision engineering, to minimize NVH levels, but achieving complete elimination can be challenging. 6. Limited Torque Handling Capability: Driveline systems have limitations in terms of torque handling capability. Excessive torque beyond the rated capacity of driveline components can lead to failures, such as shearing of gears, clutch slippage, or drive shaft breakage. High-performance vehicles or heavy-duty applications may require specialized driveline components capable of handling higher torque loads, which can increase costs and complexity. 7. Traction Limitations: Driveline systems, particularly in vehicles with two-wheel drive configurations, may experience traction limitations, especially in slippery or off-road conditions. Power is typically transmitted to only one or two wheels, which can result in reduced traction and potential wheel slippage. This limitation can be mitigated by utilizing technologies such as limited-slip differentials, electronic traction control, or implementing all-wheel drive systems. While driveline systems provide crucial power transmission and vehicle control, they do have limitations and disadvantages that need to be considered. Manufacturers, designers, and operators should carefully assess these factors and implement appropriate design, maintenance, and operational practices to optimize driveline performance, reliability, and overall vehicle functionality.
How do drivelines contribute to power transmission and motion in various applications?Drivelines play a crucial role in power transmission and motion in various applications, including automotive vehicles, agricultural machinery, construction equipment, and industrial systems. They are responsible for transmitting power from the engine or power source to the driven components, enabling motion and providing the necessary torque to perform specific tasks. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drivelines contribute to power transmission and motion in various applications: 1. Automotive Vehicles: In automotive vehicles, such as cars, trucks, and motorcycles, drivelines transmit power from the engine to the wheels, enabling motion and propulsion. The driveline consists of components such as the engine, transmission, drive shafts, differentials, and axles. The engine generates power by burning fuel, and this power is transferred to the transmission. The transmission selects the appropriate gear ratio and transfers power to the drive shafts. The drive shafts transmit the power to the differentials, which distribute it to the wheels. The wheels, in turn, convert the rotational power into linear motion, propelling the vehicle forward or backward. 2. Agricultural Machinery: Drivelines are extensively used in agricultural machinery, such as tractors, combines, and harvesters. These machines require power transmission to perform various tasks, including plowing, tilling, planting, and harvesting. The driveline in agricultural machinery typically consists of a power take-off (PTO) unit, drive shafts, gearboxes, and implement shafts. The PTO unit connects to the tractor’s engine and transfers power to the drive shafts. The drive shafts transmit power to the gearboxes, which further distribute it to the implement shafts. The implement shafts drive the specific agricultural implements, enabling them to perform their intended functions. 3. Construction Equipment: Drivelines are essential in construction equipment, such as excavators, loaders, bulldozers, and cranes. These machines require power transmission to perform tasks such as digging, lifting, pushing, and hauling. The driveline in construction equipment typically consists of an engine, transmission, drive shafts, hydraulic systems, and various gear mechanisms. The engine generates power, which is transferred to the transmission. The transmission, along with the hydraulic systems and gear mechanisms, converts and controls the power to drive the different components of the equipment, allowing them to perform their specific functions. 4. Industrial Systems: Drivelines are widely used in industrial systems and machinery, including conveyor systems, manufacturing equipment, and heavy-duty machinery. These applications require power transmission for material handling, processing, and production. The driveline in industrial systems often involves electric motors, gearboxes, drive shafts, couplings, and driven components. The electric motor provides rotational power, which is transmitted through the driveline components to drive the machinery or conveyors, facilitating the desired motion and power transmission within the industrial system. 5. Power Generation: Drivelines are also employed in power generation applications, such as generators and turbines. These systems require power transmission to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. The driveline in power generation often consists of a prime mover, such as an internal combustion engine or a steam turbine, connected to a generator. The driveline components, such as couplings, gearboxes, and drive shafts, transmit the rotational power from the prime mover to the generator, which converts it into electrical power. 6. Marine and Aerospace Applications: Drivelines are utilized in marine vessels and aerospace systems to facilitate propulsion and motion. In marine applications, drivelines transfer power from engines or turbines to propellers or water jets, enabling the vessel to move through the water. In aerospace applications, drivelines transmit power from engines to various components, such as rotors or propellers, providing the necessary thrust for flight. In summary, drivelines are integral to power transmission and motion in a wide range of applications. They enable the transfer of power from the engine or power source to the driven components, allowing for the generation of torque and the performance of specific tasks. Drivelines play a vital role in automotive vehicles, agricultural machinery, construction equipment, industrial systems, power generation, and marine and aerospace applications, contributing to efficient power transmission, motion, and the overall functionality of these diverse systems.
China Best Sales Customized High Precision Spare Parts Auto/Truck/Drive/Gear/Spline/Propeller/Half/Sleeve/Machinery/Sliding/Transmission Axle Shaft 42CrMo 20crmoti Drive LineProduct Description
Customized High Precision Spare Parts Auto/Truck/Drive/Gear/Spline/Propeller/Half/Sleeve/Machinery/Sliding/Transmission Axle Shaft 42CrMo 20CrMoTi
(1) Accessory products of the truck, the product quality is stable and reliable.
Factory Show More Products
Function Heavy trucks usually have double rear axles. If they are driven separately, they need to use 2 transmission shafts or add a transfer case at the output of the gearbox, which is heavy and cumbersome. Now a through shaft is designed in the middle axle to solve this problem. Only 1 transmission shaft is needed to drive 2 rear axles at the same time. Packaging & Shipping Exhibition FAQ Q1. Are you a factory or trading company? Q2. What are the advantages of your products? Q3. How about products price? Q4. What is your terms of packing? Q5. How to guarantee your after-sales service? Certifications /* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
How do drivelines ensure optimal power transfer while minimizing energy losses?Drivelines play a crucial role in ensuring optimal power transfer from the engine to the wheels while minimizing energy losses. The design and components of the driveline system are carefully engineered to maximize efficiency and minimize power wastage. Here are some key factors that contribute to achieving optimal power transfer and minimizing energy losses within a driveline: 1. Efficient Power Transmission: Drivelines utilize various components, such as transmissions, clutches, and torque converters, to transmit power from the engine to the wheels. These components are designed to minimize energy losses by reducing friction, improving gear mesh efficiency, and optimizing torque transfer. For example, using low-friction materials, such as roller bearings, and employing advanced gear designs, like helical or hypoid gears, can help reduce power losses due to friction and gear meshing. 2. Gear Ratio Optimization: The selection of appropriate gear ratios is essential for achieving optimal power transfer. By choosing gear ratios that match the engine’s power characteristics and the vehicle’s driving conditions, the driveline can efficiently convert and transmit power to the wheels. Optimized gear ratios ensure that the engine operates within its optimal RPM range, reducing unnecessary power losses and improving overall efficiency. 3. Limited Slip Differentials: In driveline systems with multiple driven wheels (such as all-wheel drive or four-wheel drive), limited slip differentials (LSDs) are often employed to distribute power between the wheels. LSDs allow for better traction by transferring torque to the wheels with more grip while minimizing energy losses. By allowing some degree of differential wheel speed, LSDs ensure power is efficiently transmitted to the wheels that can utilize it most effectively. 4. Hybrid and Electric Drivetrains: In hybrid and electric drivetrains, driveline systems are designed to optimize power transfer and minimize energy losses specific to the characteristics of electric motors and energy storage systems. These drivetrains often utilize sophisticated power electronics, regenerative braking systems, and advanced control algorithms to efficiently manage power flow and energy regeneration, resulting in improved overall system efficiency. 5. Aerodynamic Considerations: Drivelines can also contribute to optimal power transfer by considering aerodynamic factors. By minimizing air resistance through streamlined vehicle designs, efficient cooling systems, and appropriate underbody airflow management, drivelines help reduce the power required to overcome aerodynamic drag. This, in turn, improves overall driveline efficiency and minimizes energy losses. 6. Advanced Control Systems: The integration of advanced control systems within drivelines allows for optimized power transfer and efficient operation. Electronic control units (ECUs) monitor various parameters such as throttle position, vehicle speed, and driving conditions to adjust power distribution, manage gear shifts, and optimize torque delivery. By continuously adapting to real-time conditions, these control systems help maximize power transfer efficiency and minimize energy losses. 7. Material Selection and Weight Reduction: The choice of materials and weight reduction strategies in driveline components contribute to minimizing energy losses. Lightweight materials, such as aluminum or composites, reduce the overall weight of the driveline system, resulting in reduced inertia and lower power requirements. Additionally, reducing the weight of rotating components, such as driveshafts or flywheels, helps improve driveline efficiency by minimizing energy losses associated with rotational inertia. 8. Regular Maintenance and Lubrication: Proper maintenance and lubrication of driveline components are essential for minimizing energy losses. Regular maintenance ensures that driveline components, such as bearings and gears, are in optimal condition, minimizing frictional losses. Additionally, using high-quality lubricants and maintaining appropriate lubrication levels reduces friction and wear, improving driveline efficiency. By incorporating these design considerations and engineering techniques, drivelines can achieve optimal power transfer while minimizing energy losses. This leads to improved overall efficiency, enhanced fuel economy, and reduced environmental impact.
How do drivelines handle variations in speed and direction during operation?Drivelines are designed to handle variations in speed and direction during operation, enabling the efficient transfer of power from the engine to the wheels. They employ various components and mechanisms to accommodate these variations and ensure smooth and reliable power transmission. Let’s explore how drivelines handle speed and direction variations: 1. Transmissions: Transmissions play a crucial role in managing speed variations in drivelines. They allow for the selection of different gear ratios to match the engine’s torque and speed with the desired vehicle speed. By shifting gears, the transmission adjusts the rotational speed and torque delivered to the driveline, enabling the vehicle to operate effectively at various speeds. Transmissions can be manual, automatic, or continuously variable, each with its own mechanism for achieving speed variation control. 2. Clutches: Clutches are used in drivelines to engage or disengage power transmission between the engine and the driveline components. They allow for smooth engagement during startup and shifting gears, as well as for disconnecting the driveline when the vehicle is stationary or the engine is idling. Clutches facilitate the control of speed variations by providing a means to temporarily interrupt power flow and smoothly transfer torque between rotating components. 3. Differential: The differential is a key component in drivelines, particularly in vehicles with multiple driven wheels. It allows the wheels to rotate at different speeds while maintaining power transfer. When a vehicle turns, the inside and outside wheels travel different distances and need to rotate at different speeds. The differential allows for this speed variation by distributing torque between the wheels, ensuring smooth operation and preventing tire scrubbing or driveline binding. 4. Universal Joints and CV Joints: Universal joints and constant velocity (CV) joints are used in drivelines to accommodate variations in direction. Universal joints are typically employed in drivelines with a driveshaft, allowing for the transmission of rotational motion even when there is an angular misalignment between the driving and driven components. CV joints, on the other hand, are used in drivelines that require constant velocity and smooth power transfer at varying angles, such as front-wheel drive vehicles. These joints allow for a consistent transfer of torque while accommodating changes in direction. 5. Transfer Cases: In drivelines with multiple axles or drivetrains, transfer cases are used to distribute power and torque to different wheels or axles. Transfer cases are commonly found in four-wheel drive or all-wheel drive systems. They allow for variations in speed and direction by proportionally distributing torque between the front and rear wheels, or between different axles, based on the traction requirements of the vehicle. 6. Electronic Control Systems: Modern drivelines often incorporate electronic control systems to further enhance speed and direction control. These systems utilize sensors, actuators, and computer algorithms to monitor and adjust power distribution, shift points, and torque delivery based on various inputs, such as vehicle speed, throttle position, wheel slip, and road conditions. Electronic control systems enable precise and dynamic management of speed and direction variations, improving traction, fuel efficiency, and overall driveline performance. By integrating transmissions, clutches, differentials, universal joints, CV joints, transfer cases, and electronic control systems, drivelines effectively handle variations in speed and direction during operation. These components and mechanisms work together to ensure smooth power transmission, optimized performance, and enhanced vehicle control in a wide range of driving conditions and applications.
How do drivelines contribute to power transmission and motion in various applications?Drivelines play a crucial role in power transmission and motion in various applications, including automotive vehicles, agricultural machinery, construction equipment, and industrial systems. They are responsible for transmitting power from the engine or power source to the driven components, enabling motion and providing the necessary torque to perform specific tasks. Here’s a detailed explanation of how drivelines contribute to power transmission and motion in various applications: 1. Automotive Vehicles: In automotive vehicles, such as cars, trucks, and motorcycles, drivelines transmit power from the engine to the wheels, enabling motion and propulsion. The driveline consists of components such as the engine, transmission, drive shafts, differentials, and axles. The engine generates power by burning fuel, and this power is transferred to the transmission. The transmission selects the appropriate gear ratio and transfers power to the drive shafts. The drive shafts transmit the power to the differentials, which distribute it to the wheels. The wheels, in turn, convert the rotational power into linear motion, propelling the vehicle forward or backward. 2. Agricultural Machinery: Drivelines are extensively used in agricultural machinery, such as tractors, combines, and harvesters. These machines require power transmission to perform various tasks, including plowing, tilling, planting, and harvesting. The driveline in agricultural machinery typically consists of a power take-off (PTO) unit, drive shafts, gearboxes, and implement shafts. The PTO unit connects to the tractor’s engine and transfers power to the drive shafts. The drive shafts transmit power to the gearboxes, which further distribute it to the implement shafts. The implement shafts drive the specific agricultural implements, enabling them to perform their intended functions. 3. Construction Equipment: Drivelines are essential in construction equipment, such as excavators, loaders, bulldozers, and cranes. These machines require power transmission to perform tasks such as digging, lifting, pushing, and hauling. The driveline in construction equipment typically consists of an engine, transmission, drive shafts, hydraulic systems, and various gear mechanisms. The engine generates power, which is transferred to the transmission. The transmission, along with the hydraulic systems and gear mechanisms, converts and controls the power to drive the different components of the equipment, allowing them to perform their specific functions. 4. Industrial Systems: Drivelines are widely used in industrial systems and machinery, including conveyor systems, manufacturing equipment, and heavy-duty machinery. These applications require power transmission for material handling, processing, and production. The driveline in industrial systems often involves electric motors, gearboxes, drive shafts, couplings, and driven components. The electric motor provides rotational power, which is transmitted through the driveline components to drive the machinery or conveyors, facilitating the desired motion and power transmission within the industrial system. 5. Power Generation: Drivelines are also employed in power generation applications, such as generators and turbines. These systems require power transmission to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. The driveline in power generation often consists of a prime mover, such as an internal combustion engine or a steam turbine, connected to a generator. The driveline components, such as couplings, gearboxes, and drive shafts, transmit the rotational power from the prime mover to the generator, which converts it into electrical power. 6. Marine and Aerospace Applications: Drivelines are utilized in marine vessels and aerospace systems to facilitate propulsion and motion. In marine applications, drivelines transfer power from engines or turbines to propellers or water jets, enabling the vessel to move through the water. In aerospace applications, drivelines transmit power from engines to various components, such as rotors or propellers, providing the necessary thrust for flight. In summary, drivelines are integral to power transmission and motion in a wide range of applications. They enable the transfer of power from the engine or power source to the driven components, allowing for the generation of torque and the performance of specific tasks. Drivelines play a vital role in automotive vehicles, agricultural machinery, construction equipment, industrial systems, power generation, and marine and aerospace applications, contributing to efficient power transmission, motion, and the overall functionality of these diverse systems.
China Hot selling Precision Transmission /Drive/Axle/Auto/Spline/Machinery Parts/ Rotor Gear Customized Machining Knurling Shaft Drive LineProduct Description
Precision Shaft by CNC Turning Machining Our advantage: *Specialization in CNC formulations of high precision and quality Production machine: Inspection equipment : Certificate:
/* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
How do manufacturers ensure the compatibility of driveline components with different vehicles?Manufacturers employ various measures to ensure the compatibility of driveline components with different vehicles. These measures involve careful design, engineering, testing, and standardization processes to meet the specific requirements of each vehicle type. Let’s explore how manufacturers ensure compatibility: 1. Vehicle-Specific Design: Manufacturers design driveline components with specific vehicle types in mind. Each vehicle type, such as passenger cars, trucks, SUVs, or commercial vehicles, has unique requirements in terms of power output, torque capacity, weight distribution, space constraints, and intended usage. Manufacturers consider these factors during the component design phase to ensure that the driveline components are optimized for compatibility with the intended vehicle type. 2. Engineering and Simulation: Manufacturers employ advanced engineering techniques and simulation tools to evaluate the performance and compatibility of driveline components. They use computer-aided design (CAD) software and finite element analysis (FEA) simulations to model and analyze the behavior of the components under various operating conditions. This allows them to identify any potential compatibility issues, such as excessive stress, misalignment, or interference, and make necessary design adjustments before moving to the production stage. 3. Prototyping and Testing: Manufacturers create prototypes of driveline components and subject them to rigorous testing to ensure compatibility. These tests include bench testing, dynamometer testing, and vehicle-level testing. By simulating real-world operating conditions, manufacturers can evaluate the performance, durability, and compatibility of the components. They assess factors such as power transmission efficiency, torque capacity, heat dissipation, noise and vibration levels, and overall drivability to ensure that the components meet the requirements and are compatible with the intended vehicle. 4. Standardization: Manufacturers adhere to industry standards and specifications to ensure compatibility and interchangeability of driveline components. These standards cover various aspects such as dimensions, material properties, spline profiles, shaft diameters, and mounting interfaces. By following established standards, manufacturers can ensure that their driveline components can be seamlessly integrated into different vehicles from various manufacturers, promoting compatibility and ease of replacement or upgrade. 5. Collaborative Development: Manufacturers often collaborate closely with vehicle manufacturers during the development process to ensure compatibility. This collaboration involves sharing specifications, design requirements, and performance targets. By working together, driveline manufacturers can align their component designs with the vehicle manufacturer’s specifications, ensuring that the driveline components fit within the vehicle’s space constraints, mating interfaces, and intended usage. This collaborative approach helps optimize compatibility and integration between the driveline components and the vehicle’s overall system. 6. Continuous Improvement: Manufacturers continuously improve their driveline components based on feedback, field data, and advancements in technology. They gather information from vehicle manufacturers, end-users, and warranty claims to identify any compatibility issues or performance shortcomings. This feedback loop helps drive refinements and enhancements in the design, manufacturing processes, and material selection of the driveline components, ensuring better compatibility and performance in future iterations. Overall, manufacturers employ a combination of vehicle-specific design, engineering and simulation, prototyping and testing, standardization, collaborative development, and continuous improvement to ensure the compatibility of driveline components with different vehicles. These efforts help optimize power transmission, reliability, and performance, while ensuring a seamless integration of the driveline components into the diverse range of vehicles present in the market.
Are there any limitations or disadvantages associated with driveline systems?While driveline systems offer numerous advantages in terms of power transmission and vehicle performance, there are also some limitations and disadvantages associated with their use. It’s important to consider these factors when designing, operating, and maintaining driveline systems. Let’s explore some of the limitations and disadvantages: 1. Complex Design and Integration: Driveline systems can be complex in design, especially in modern vehicles with advanced technologies. They often consist of multiple components, such as transmissions, differentials, transfer cases, and drive shafts, which need to be properly integrated and synchronized. The complexity of the driveline system can increase manufacturing and assembly challenges, as well as the potential for compatibility issues or failures if not designed and integrated correctly. 2. Energy Losses: Driveline systems can experience energy losses during power transmission. These losses occur due to factors such as friction, heat generation, mechanical inefficiencies, and fluid drag in components like gearboxes, differentials, and torque converters. The energy losses can negatively impact overall efficiency and result in reduced fuel economy or power output, especially in systems with multiple driveline components. 3. Limited Service Life and Maintenance Requirements: Driveline components, like any mechanical system, have a limited service life and require regular maintenance. Components such as clutches, bearings, gears, and drive shafts are subject to wear and tear, and may need to be replaced or repaired over time. Regular maintenance, including lubrication, adjustments, and inspections, is necessary to ensure optimal performance and prevent premature failures. Failure to perform proper maintenance can lead to driveline malfunctions, increased downtime, and costly repairs. 4. Weight and Space Constraints: Driveline systems add weight and occupy space within a vehicle. The additional weight affects fuel efficiency and overall vehicle performance. Moreover, the space occupied by driveline components can limit design flexibility, particularly in compact or electric vehicles where space optimization is crucial. Manufacturers must strike a balance between driveline performance, vehicle weight, and available space to meet the requirements of each specific vehicle type. 5. Noise, Vibration, and Harshness (NVH): Driveline systems can generate noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH) during operation. Factors such as gear meshing, unbalanced rotating components, or improper driveline alignment can contribute to unwanted vibrations or noise. NVH issues can affect driving comfort, passenger experience, and vehicle refinement. Manufacturers employ various techniques, including vibration dampening materials, isolators, and precision engineering, to minimize NVH levels, but achieving complete elimination can be challenging. 6. Limited Torque Handling Capability: Driveline systems have limitations in terms of torque handling capability. Excessive torque beyond the rated capacity of driveline components can lead to failures, such as shearing of gears, clutch slippage, or drive shaft breakage. High-performance vehicles or heavy-duty applications may require specialized driveline components capable of handling higher torque loads, which can increase costs and complexity. 7. Traction Limitations: Driveline systems, particularly in vehicles with two-wheel drive configurations, may experience traction limitations, especially in slippery or off-road conditions. Power is typically transmitted to only one or two wheels, which can result in reduced traction and potential wheel slippage. This limitation can be mitigated by utilizing technologies such as limited-slip differentials, electronic traction control, or implementing all-wheel drive systems. While driveline systems provide crucial power transmission and vehicle control, they do have limitations and disadvantages that need to be considered. Manufacturers, designers, and operators should carefully assess these factors and implement appropriate design, maintenance, and operational practices to optimize driveline performance, reliability, and overall vehicle functionality.
Which industries and vehicles commonly use drivelines for power distribution?Drivelines are widely used in various industries and vehicles for power distribution. They play a crucial role in transmitting power from the engine or power source to the driven components, enabling motion and torque transfer. Here’s a detailed explanation of the industries and vehicles that commonly utilize drivelines for power distribution: 1. Automotive Industry: The automotive industry extensively utilizes drivelines in passenger cars, commercial vehicles, and off-road vehicles. Drivelines are a fundamental component of vehicles, enabling power transmission from the engine to the wheels. They are found in a range of vehicle types, including sedans, SUVs, pickup trucks, vans, buses, and heavy-duty trucks. Drivelines in the automotive industry are designed to provide efficient power distribution, enhance vehicle performance, and ensure smooth acceleration and maneuverability. 2. Agricultural Industry: Drivelines are essential in the agricultural industry for various farming machinery and equipment. Tractors, combines, harvesters, and other agricultural machinery rely on drivelines to transfer power from the engine to the wheels or tracks. Drivelines in agricultural equipment often incorporate power take-off (PTO) units, allowing the connection of implements such as plows, seeders, and balers. These drivelines are designed to handle high torque loads, provide traction in challenging field conditions, and facilitate efficient farming operations. 3. Construction and Mining Industries: Drivelines are extensively used in construction and mining equipment, where they enable power distribution and mobility in heavy-duty machinery. Excavators, bulldozers, wheel loaders, dump trucks, and other construction and mining vehicles rely on drivelines to transfer power from the engine to the wheels or tracks. Drivelines in these industries are designed to withstand rigorous operating conditions, deliver high torque and traction, and provide the necessary power for excavation, hauling, and material handling tasks. 4. Industrial Equipment: Various industrial equipment and machinery utilize drivelines for power distribution. This includes material handling equipment such as forklifts and cranes, industrial trucks, conveyor systems, and industrial vehicles used in warehouses, factories, and distribution centers. Drivelines in industrial equipment are designed to provide efficient power transmission, precise control, and maneuverability in confined spaces, enabling smooth and reliable operation in industrial settings. 5. Off-Road and Recreational Vehicles: Drivelines are commonly employed in off-road and recreational vehicles, including all-terrain vehicles (ATVs), side-by-side vehicles (UTVs), dirt bikes, snowmobiles, and recreational boats. These vehicles require drivelines to transfer power from the engine to the wheels, tracks, or propellers, enabling off-road capability, traction, and water propulsion. Drivelines in off-road and recreational vehicles are designed for durability, performance, and enhanced control in challenging terrains and recreational environments. 6. Railway Industry: Drivelines are utilized in railway locomotives and trains for power distribution and propulsion. They are responsible for transmitting power from the locomotive’s engine to the wheels or driving systems, enabling the movement of trains on tracks. Drivelines in the railway industry are designed to handle high torque requirements, ensure efficient power transfer, and facilitate safe and reliable train operation. 7. Marine Industry: Drivelines are integral components in marine vessels, including boats, yachts, ships, and other watercraft. Marine drivelines are used for power transmission from the engine to the propellers or water jets, providing thrust and propulsion. They are designed to withstand the corrosive marine environment, handle high torque loads, and ensure efficient power transfer for marine propulsion. These are some of the industries and vehicles that commonly rely on drivelines for power distribution. Drivelines are versatile components that enable efficient power transmission, mobility, and performance across a wide range of applications, contributing to the functionality and productivity of various industries and vehicles.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||


